In news you can use: the Food and Drug Administration has decided to eliminate trans fats from the American diet. What does this mean? Why should you care? Read on…
Substances known as trans fats, trans fatty acids or partially hydrogenated oils serve the purpose of making liquid vegetable oils more solid. You know and love them because they make food taste good. It’s largely why some of you love and crave foods that are deep fried. What types of foods am I describing? Think about French fries, pizza, pies, doughnuts, pastries, microwave popcorn, cookies and popcorn creamer. Are you using stick margarine? Not for long! Enjoy it while it lasts – or better yet, don’t.
Trans fats raise your bad (LDL) cholesterol levels and lower your good (HDL) cholesterol levels. Eating trans fats increases your risk of developing heart disease and stroke. It’s also associated with a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
This move will eliminate 20,000 heart attacks and 7,000 deaths due to heart disease per year. However, you know what won’t die? Your taste buds. Options always exist, and food manufacturers will find healthier ways to make food just as tasty as it has always been. By the way, you can do the same even now with just a little effort.
Before you start thinking about whether you can ingest trans fats in moderation, the answer is no. Trans fats occur in sufficient amounts naturally that you’re already eating the limits of what would be acceptable. Adding industrially made trans fats simply adds to your risk of disease and avoidable death.
Now if we can only get you to exercise…
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) offers. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Tag Archives: United States
Straight, No Chaser: Bye-Bye, Trans Fats
Straight, No Chaser: Save a Life, Save a Trip, Save Your Cash!
In the last 20+ years of caring for patients in emergency rooms (ERs) in communities all over the country, and in 12 years of healthcare consulting in 36 states and countries, my team and I have had the unique privilege of serving all age groups, genders, and health conditions, from sprains to strains, moans and groans, sniffles and whistles, trauma and the flu.
However, in the ER setting, well over half of the people we see every single day would say they could have saved themselves the trip and the cost “…if I only knew.” Straight, No Chaser has given me the privilege to talk with you in a relaxed environment about urgent and non-urgent issues that concern you. It has been fun for me, especially because you have responded in a way that lets me know that my goal of empowering you with knowledge to make your own healthcare and financial decisions for you and your family is being realized. Because this works for your health and your wallet, I have expanded the service from Straight, No Chaser to http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com. Not only will you have access to thousands of tips, fun facts, and frequently asked questions about the full spectrum of health topics, you will also have access to your own personal healthcare consulting team. That’s right, you can chat 24/7 with experts in medicine as well as fitness, dentistry, nutrition, mental health, pharmacy, and other healthcare entities.
So, when the time comes that you need to make an informed decision for yourself and/or your family member, we’re here for you. If this turns out as we desire, this service will become part of the national healthcare system and may be covered by your current insurance interests or as an employee benefit. Beginning today, November 1 at 12 noon Eastern Daylight Time, join me and hundreds of other healthcare experts who have signed up to turn the tide in our country by putting the power of your health back in your hands and saving you the time and costs of unnecessary visits to the emergency room and pharmacy. A subscription counts as payment toward your deductible (if you have insurance) and equates to less than a third of what Americans pay out-of-pocket EVERY YEAR for ER and doctor visits. Try us, and discover the difference having a team at your fingertips will make in your health. We at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com are looking forward to keeping the knowledge flowing,
Jeffrey Sterling, MD
President and CEO
SterlingMedicalAdvice.com
Your Personal and Immediate 24-Hour HealthCare Consultants
In the last 20+ years of caring for patients in emergency rooms (ERs) in communities all over the country, and in 12 years of healthcare consulting in 36 states and countries, my team and I have had the unique privilege of serving all age groups, genders, and health conditions, from sprains to strains, moans and groans, sniffles and whistles, trauma and the flu.
However, in the ER setting, well over half of the people we see every single day would say they could have saved themselves the trip and the cost “…if I only knew.” Straight, No Chaser has given me the privilege to talk with you in a relaxed environment about urgent and non-urgent issues that concern you. It has been fun for me, especially because you have responded in a way that lets me know that my goal of empowering you with knowledge to make your own healthcare and financial decisions for you and your family is being realized. Because this works for your health and your wallet, I have expanded the service from Straight, No Chaser to http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com. Not only will you have access to thousands of tips, fun facts, and frequently asked questions about the full spectrum of health topics, you will also have access to your own personal healthcare consulting team. That’s right, you can chat 24/7 with experts in medicine as well as fitness, dentistry, nutrition, mental health, pharmacy, and other healthcare entities.
So, when the time comes that you need to make an informed decision for yourself and/or your family member, we’re here for you. If this turns out as we desire, this service will become part of the national healthcare system and may be covered by your current insurance interests or as an employee benefit. Beginning today, November 1 at 12 noon Eastern Daylight Time, join me and hundreds of other healthcare experts who have signed up to turn the tide in our country by putting the power of your health back in your hands and saving you the time and costs of unnecessary visits to the emergency room and pharmacy. A subscription counts as payment toward your deductible (if you have insurance) and equates to less than a third of what Americans pay out-of-pocket EVERY YEAR for ER and doctor visits. Try us, and discover the difference having a team at your fingertips will make in your health. We at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com are looking forward to keeping the knowledge flowing,
Jeffrey Sterling, MD
President and CEO
SterlingMedicalAdvice.com
Your Personal and Immediate 24-Hour HealthCare Consultants
Straight, No Chaser: A Solution to the Upcoming Healthcare Crisis and the Affordable Care Act

Many of you have heard or seen me discuss various aspects of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. This ambitious effort seeks to maintain the current level of quality that exists (via maintaining the same insurance coverage for those individuals that already have it), while adding approximately 30 million individuals to the insurance rolls while not increasing overall system costs.
Have you noticed that one part of the conversation that doesn’t seem to occur is “Who’s going to take care of these 30 million new individuals? Also, what about the other 20 million that still won’t have insurance?” The twin deterrents of co-pays and deductibles will eventually be stiffened to curtail over- and inappropriate utilization of the emergency room for both the newly insured and the uninsured voucher recipients (Besides, who wants to deal with the long wait times both in your physician’s office and the ER, soon to be even worse with all the newly insured?). Similarly, you would presume that armies of new physicians are being trained to meet this growth in the newly insured, but that simply isn’t the case. Additional options to address this influx will be necessary. Prominent among these options will be those providing better education and greater empowerment of patients to direct their own care.
Sterling Medical Advice (SMA) is a national public health initiative that provides a solution to these issues by the introduction of 24/7 online personal healthcare consulting, featuring physicians and other care professionals covering the entire spectrum of medicine and healthcare. Consultations will be personalized and immediately available to those in need around the clock.
“What’s that, and when might you use it?” Here are a few examples.
- You need advice regarding an immediate medical concern
- You need general information about your medical condition
- You need immediate information about your prescription
- You are experiencing symptoms and want to know why
- You want to learn more information about a medical condition that is part of your family history
- You want additional details on your upcoming medical procedure
- You need advice regarding the best care option for addressing a medical concern (e.g., emergency room vs. urgent care vs. scheduling an appointment with your primary care physician)
- You want a second opinion on your new diagnosis
- You want a second opinion on your new treatment plan
- You need additional information about what to expect from a newly diagnosed condition
Sterling Medical Advice will improve public health outcomes while reducing healthcare costs for individuals, families and businesses and the healthcare system at large. Personal healthcare consulting will create a better-educated and empowered population and will become an additional component to the American health care system without compromising quality.
To find out more about Sterling Medical Advice, visit www.sterlingmedicaladvice.com, and thanks for following Straight, No Chaser.

Many of you have heard or seen me discuss various aspects of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. This ambitious effort seeks to maintain the current level of quality that exists (via maintaining the same insurance coverage for those individuals that already have it), while adding approximately 30 million individuals to the insurance rolls while not increasing overall system costs.
Have you noticed that one part of the conversation that doesn’t seem to occur is “Who’s going to take care of these 30 million new individuals? Also, what about the other 20 million that still won’t have insurance?” The twin deterrents of co-pays and deductibles will eventually be stiffened to curtail over- and inappropriate utilization of the emergency room for both the newly insured and the uninsured voucher recipients (Besides, who wants to deal with the long wait times both in your physician’s office and the ER, soon to be even worse with all the newly insured?). Similarly, you would presume that armies of new physicians are being trained to meet this growth in the newly insured, but that simply isn’t the case. Additional options to address this influx will be necessary. Prominent among these options will be those providing better education and greater empowerment of patients to direct their own care.
Sterling Medical Advice (SMA) is a national public health initiative that provides a solution to these issues by the introduction of 24/7 online personal healthcare consulting, featuring physicians and other care professionals covering the entire spectrum of medicine and healthcare. Consultations will be personalized and immediately available to those in need around the clock.
“What’s that, and when might you use it?” Here are a few examples.
- You need advice regarding an immediate medical concern
- You need general information about your medical condition
- You need immediate information about your prescription
- You are experiencing symptoms and want to know why
- You want to learn more information about a medical condition that is part of your family history
- You want additional details on your upcoming medical procedure
- You need advice regarding the best care option for addressing a medical concern (e.g., emergency room vs. urgent care vs. scheduling an appointment with your primary care physician)
- You want a second opinion on your new diagnosis
- You want a second opinion on your new treatment plan
- You need additional information about what to expect from a newly diagnosed condition
Sterling Medical Advice will improve public health outcomes while reducing healthcare costs for individuals, families and businesses and the healthcare system at large. Personal healthcare consulting will create a better-educated and empowered population and will become an additional component to the American health care system without compromising quality.
To find out more about Sterling Medical Advice, visit www.sterlingmedicaladvice.com, and thanks for following Straight, No Chaser.
Straight, No Chaser: Revisiting the Affordable Care Act – How You or Your Employer Can Save Up to 50% of HealthCare Costs
Politics aside, I’m not so sure why business owners are focusing on the angst of implementation of the Affordable Care Act instead of the opportunities to save.
Consider the following from the Small Business Association website: “The Affordable Care Act (ACA) creates new incentives for employers to promote wellness among employees by creating supportive, healthier work environments and encouraging employees to take advantage of workplace wellness programs. Health-contingent wellness programs generally require employees to meet a specific standard related to their health, e.g., decreased tobacco use or lowered cholesterol levels. Under the ACA rules that take effect on January 1, 2014, employer rewards will increase from a 20–30% refund of their healthcare coverage costs for employing health-contingent programs, up to 50% for programs designed to prevent or reduce tobacco use.”
Subscribing to www.sterlingmedicaladvice.com as an employee benefit will save companies up to half of the insurance costs they are already paying for their employees. These savings can occur at a cost of less than 10% of current costs of insurance! For more information about the final rules’ flexibility in eligible wellness programs, visit www.dol.gov/ebsa. Have your employee assistance program administrator contact us at 1-866-ADVICE3 (238-4233) or email us at sales@sterlingmedicaladvice.com.
Looking to cut your ACA tax in half? Sign up with SMA, reduce absenteeism, win the appreciation of your employees, and save a bundle.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Politics aside, I’m not so sure why business owners are focusing on the angst of implementation of the Affordable Care Act instead of the opportunities to save.
Consider the following from the Small Business Association website: “The Affordable Care Act (ACA) creates new incentives for employers to promote wellness among employees by creating supportive, healthier work environments and encouraging employees to take advantage of workplace wellness programs. Health-contingent wellness programs generally require employees to meet a specific standard related to their health, e.g., decreased tobacco use or lowered cholesterol levels. Under the ACA rules that take effect on January 1, 2014, employer rewards will increase from a 20–30% refund of their healthcare coverage costs for employing health-contingent programs, up to 50% for programs designed to prevent or reduce tobacco use.”
Subscribing to www.sterlingmedicaladvice.com as an employee benefit will save companies up to half of the insurance costs they are already paying for their employees. These savings can occur at a cost of less than 10% of current costs of insurance! For more information about the final rules’ flexibility in eligible wellness programs, visit www.dol.gov/ebsa. Have your employee assistance program administrator contact us at 1-866-ADVICE3 (238-4233) or email us at sales@sterlingmedicaladvice.com.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Heads Up! Concussions – Traumatic Brain Injuries, Part I
The really interesting thing about concussions these days is many individuals seem to have convinced themselves that the risk of a concussion or even continuing in football, wrestling, boxing, or MMA type activities after having had concussions won’t deter them from pursuing the glory, fame, and fortune to be obtained in putting themselves at risk. That’s a fascinating but very flawed concept, as evidenced by the increasing suicide rate among concussed former athletes.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a blunt or penetrating head blow that disrupts some aspect of normal brain function. TBIs may produce changes, ranging from brief alterations in mental status or consciousness to an extended period of unconsciousness or amnesia. (It’s important to note that not all blows to the head result in a TBI.) For the purposes of this discussion, the majority of TBIs that occur each year are concussions. In terms of societal impact, TBIs contribute to a remarkable number of deaths and permanent disability. Every year, at least 1.7 million TBIs occur in the US.
Healthcare professionals may describe a concussion as a “mild” brain injury because concussions are usually not life threatening. Even so, their effects can be serious. Concussive symptoms usually fall in one of four categories:
- Thinking/remembering
- Physical
- Emotional/mood
- Sleep
Red Flags
Get to the ER right away if you have any of the following danger signs after any type of head injury, no matter how minor it may seem:
- Any difficulty waking
- Any loss of consciousness, confusion, or significant agitation
- One pupil (the black part in the middle of the eye) larger than the other
- Loss of ability to identify people, places, the date, or self
- Loss of motion or sensation, weakness, numbness or loss of coordination
- Persistent, worsening headache
- Repeated vomiting
- Slurred speech or difficulty with expression
- Seizures
- Kids will not stop crying and cannot be consoled
- Kids will not nurse or eat
Click here for Part II, in which we discuss complications and treatment options.
Click here for Part III, in which a neurologist adds his thoughts.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
The really interesting thing about concussions these days is many individuals seem to have convinced themselves that the risk of a concussion or even continuing in football, wrestling, boxing, or MMA type activities after having had concussions won’t deter them from pursuing the glory, fame, and fortune to be obtained in putting themselves at risk. That’s a fascinating but very flawed concept, as evidenced by the increasing suicide rate among concussed former athletes.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a blunt or penetrating head blow that disrupts some aspect of normal brain function. TBIs may produce changes, ranging from brief alterations in mental status or consciousness to an extended period of unconsciousness or amnesia. (It’s important to note that not all blows to the head result in a TBI.) For the purposes of this discussion, the majority of TBIs that occur each year are concussions. In terms of societal impact, TBIs contribute to a remarkable number of deaths and permanent disability. Every year, at least 1.7 million TBIs occur in the US.
Healthcare professionals may describe a concussion as a “mild” brain injury because concussions are usually not life threatening. Even so, their effects can be serious. Concussive symptoms usually fall in one of four categories:
- Thinking/remembering
- Physical
- Emotional/mood
- Sleep
Red Flags
Get to the ER right away if you have any of the following danger signs after any type of head injury, no matter how minor it may seem:
- Any difficulty waking
- Any loss of consciousness, confusion, or significant agitation
- One pupil (the black part in the middle of the eye) larger than the other
- Loss of ability to identify people, places, the date, or self
- Loss of motion or sensation, weakness, numbness or loss of coordination
- Persistent, worsening headache
- Repeated vomiting
- Slurred speech or difficulty with expression
- Seizures
- Kids will not stop crying and cannot be consoled
- Kids will not nurse or eat
Click here for Part II, in which we discuss complications and treatment options.
Click here for Part III, in which a neurologist adds his thoughts.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Heads Up! Traumatic Brain Injuries (Concussions), Part I

Human Shark Week continues with a discussion about concussions. The really interesting thing about concussions these days is many individuals seem to have convinced themselves that the risk of a concussion or even continuing in football, wrestling, boxing or MMA type activities after having had concussions won’t deter them from pursuing the glory, fame and fortune to be obtained in putting themselves at risk. That’s a fascinating but very flawed concept, as evidenced by the increasing suicide rate among concussed former athletes.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a blunt or penetrating head blow that disrupts some aspect of normal brain function. TBIs may produce changes ranging from brief alterations in mental status or consciousness to an extended period of unconsciousness or amnesia (It’s important to note that not all blows to the head result in a TBI.). For the purposes of this discussion, the majority of TBIs that occur each year are concussions. In terms of societal impact, TBIs contributes to a remarkable number of deaths and permanent disability. Every year, at least 1.7 million TBIs occur in the US.
Health care professionals may describe a concussion as a “mild” brain injury because concussions are usually not life threatening. Even so, their effects can be serious. Concussive symptoms usually fall in one of four categories:
- Thinking/remembering
- Physical
- Emotional/mood
- Sleep
Red Flags:
Get to the ER right away if you have any of the following danger signs after any type of head injury, no matter how minor it may seem:
- Any difficulty being awakened
- Any loss of consciousness, confusion or significant agitation
- Have one pupil (the black part in the middle of the eye) larger than the other
- Loss of ability to recognize people, places or inability to identify the date or themselves
- Loss of motion or sensation, weakness, numbness or loss of coordination
- Persistent, worsening headache
- Repeated vomiting.
- Slurred speech or difficulty with expression
- Seizures
- Kids will not stop crying and cannot be consoled
- Kids will not nurse or eat
This afternoon, in Part II, we will discuss complications and treatment options.

Human Shark Week continues with a discussion about concussions. The really interesting thing about concussions these days is many individuals seem to have convinced themselves that the risk of a concussion or even continuing in football, wrestling, boxing or MMA type activities after having had concussions won’t deter them from pursuing the glory, fame and fortune to be obtained in putting themselves at risk. That’s a fascinating but very flawed concept, as evidenced by the increasing suicide rate among concussed former athletes.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is caused by a blunt or penetrating head blow that disrupts some aspect of normal brain function. TBIs may produce changes ranging from brief alterations in mental status or consciousness to an extended period of unconsciousness or amnesia (It’s important to note that not all blows to the head result in a TBI.). For the purposes of this discussion, the majority of TBIs that occur each year are concussions. In terms of societal impact, TBIs contributes to a remarkable number of deaths and permanent disability. Every year, at least 1.7 million TBIs occur in the US.
Health care professionals may describe a concussion as a “mild” brain injury because concussions are usually not life threatening. Even so, their effects can be serious. Concussive symptoms usually fall in one of four categories:
- Thinking/remembering
- Physical
- Emotional/mood
- Sleep
Red Flags:
Get to the ER right away if you have any of the following danger signs after any type of head injury, no matter how minor it may seem:
- Any difficulty being awakened
- Any loss of consciousness, confusion or significant agitation
- Have one pupil (the black part in the middle of the eye) larger than the other
- Loss of ability to recognize people, places or inability to identify the date or themselves
- Loss of motion or sensation, weakness, numbness or loss of coordination
- Persistent, worsening headache
- Repeated vomiting.
- Slurred speech or difficulty with expression
- Seizures
- Kids will not stop crying and cannot be consoled
- Kids will not nurse or eat
This afternoon, in Part II, we will discuss complications and treatment options.
Straight, No Chaser: Quick Tip – Caring for Your Ankle Sprain

If you decide not to come to the Emergency Room for your ankle sprain, just think about the mnemonic “RICE.” (This works for any other soft tissue sprain, such as the wrist.)
Rest
The longer you stay off of it, the quicker it will heal. The more you try to use it, the longer your recovery will take and the greater the risk of aggravating the injury.
Ice
Apply ice for 15–20 minutes every hour over the first 24 hours. That will help keep the swelling and pain down. However, please keep a towel between the ice pack and your skin.
Compression/Crutches
Use an ace wrap for comfort and to help with the swelling. Use crutches to help stay off that ankle.
Elevation
This is about the only time I’ll tell you it’s ok to be a couch potato. Keep your leg elevated on the bed or on the couch at or above the level of your chest. That’ll help to keep the swelling down.
If you go to the ER, we’ll do the same for you, unless you have a fracture somewhere, in which case we’ll splint or cast you instead giving you the ace wrap. Stay safe.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

If you decide not to come to the Emergency Room for your ankle sprain, just think about the mnemonic “RICE.” (This works for any other soft tissue sprain, such as the wrist.)
Rest
The longer you stay off of it, the quicker it will heal. The more you try to use it, the longer your recovery will take and the greater the risk of aggravating the injury.
Ice
Apply ice for 15–20 minutes every hour over the first 24 hours. That will help keep the swelling and pain down. However, please keep a towel between the ice pack and your skin.
Compression/Crutches
Use an ace wrap for comfort and to help with the swelling. Use crutches to help stay off that ankle.
Elevation
This is about the only time I’ll tell you it’s ok to be a couch potato. Keep your leg elevated on the bed or on the couch at or above the level of your chest. That’ll help to keep the swelling down.
If you go to the ER, we’ll do the same for you, unless you have a fracture somewhere, in which case we’ll splint or cast you instead giving you the ace wrap. Stay safe.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: That Doesn't Belong There, Little Johnny!
Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: That Doesn't Belong There, Little Johnny
Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
Straight, No Chaser: The Reach of Breast Cancer and Your Risk Factors
Even as a physician, I am left to think about the horror of being a woman with a lifetime risk of acquiring breast cancer that’s 1 in 8. The only thing I can think of off-hand and relate to similarly is the risk for trauma being an inner-city minority kid. This risk of breast cancer is compounded by the reality that there is no way to prevent it. Thus, it must be emphasized early and often: risk factor identification and reduction, coupled with early evaluation, detection and treatment are absolutely vital.
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer contracted by American women (after skin cancer), and it is the second most common cause of death from cancer (after lung cancer). More than a quarter of a million new cases will be diagnosed in women yearly, and approximately 40,000 women will die from complications of breast cancer annually (that’s over 100 deaths every day).
In the event the previous information seemed like too much gloom and doom, understand that the tide has been stemmed. After more than two decades of increase, rates of new cases of breast cancer began dropping in 2000 and have stabilized. This is largely thought to be due to declining rates of post-menopausal hormone use in response to results from major research projects. As you may know, such hormone use has been shown to increase the risk of both breast cancer and heart disease.
Speaking of risks, I don’t especially like this part of the conversation because it always comes across as if everything is a risk factor, and there are still controversies about what is or isn’t a risk. As a result, patients end up confused and paralyzed into inaction. Therefore, I’ll mention just enough for you to understand and work with; if you have specific questions on what you’ve heard that I haven’t already addressed in the breast cancer myth posts (Parts I and II), feel free to ask.
There are risk factors you can’t change, like aging, family history and being a woman. Having these risk factors simply means you need to be more diligent in performing self exams and seeking early care for suspicious findings. Now, there are other risk factors you can minimize. Oral contraceptive use, postmenopausal hormonal therapy, choosing not to breast feed, alcohol use and obesity are all risk factors for breast cancer that are under your control.
The bottom line is your risk factors don’t cause cancer, and the absence of risk factors doesn’t ensure you won’t have breast cancer. For example, men contract breast cancer as well. What it all comes down to is you must be diligent in performing exams and getting evaluated and treated if something abnormal is discovered. We’ll discuss some of that next.
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer contracted by American women (after skin cancer), and it is the second most common cause of death from cancer (after lung cancer). More than a quarter of a million new cases will be diagnosed in women yearly, and approximately 40,000 women will die from complications of breast cancer annually (that’s over 100 deaths every day).
In the event the previous information seemed like too much gloom and doom, understand that the tide has been stemmed. After more than two decades of increase, rates of new cases of breast cancer began dropping in 2000 and have stabilized. This is largely thought to be due to declining rates of post-menopausal hormone use in response to results from major research projects. As you may know, such hormone use has been shown to increase the risk of both breast cancer and heart disease.
Speaking of risks, I don’t especially like this part of the conversation because it always comes across as if everything is a risk factor, and there are still controversies about what is or isn’t a risk. As a result, patients end up confused and paralyzed into inaction. Therefore, I’ll mention just enough for you to understand and work with; if you have specific questions on what you’ve heard that I haven’t already addressed in the breast cancer myth posts (Parts I and II), feel free to ask.
There are risk factors you can’t change, like aging, family history and being a woman. Having these risk factors simply means you need to be more diligent in performing self exams and seeking early care for suspicious findings. Now, there are other risk factors you can minimize. Oral contraceptive use, postmenopausal hormonal therapy, choosing not to breast feed, alcohol use and obesity are all risk factors for breast cancer that are under your control.
The bottom line is your risk factors don’t cause cancer, and the absence of risk factors doesn’t ensure you won’t have breast cancer. For example, men contract breast cancer as well. What it all comes down to is you must be diligent in performing exams and getting evaluated and treated if something abnormal is discovered. We’ll discuss some of that next.
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: (El)even More Myths Regarding Breast Cancer
Continuing from the earlier post with additional myths, well because you have so many questions! In fact, I’m doubling up on what you received earlier in Part I of Breast Cancer Myths.
6. “Breast cancer is preventable.”
- Unfortunately, this is not true. All of our efforts are geared toward lowering risks, early detection and effective treatment.
7. The risk of breast cancer isn’t affected by obesity.
- Not true. The risk is particularly increased in post-menopausal women with weight gain.
8. African-American women have an increased risk due to hair straighteners and relaxers.
- This myth was taken head on and debunked by the National Cancer Institute in a large 2007 study including women with significant use over a 20-year period.
9. Caffeine causes breast cancer.
- Not according to the evidence. There’s even evidence suggesting a benefit, but the data on this is just as inconclusive as that suggesting a link to breast cancer.
10. Mammograms increase breast cancer risk due to the radiation load.
- The risks of radiation are so relatively insignificant that they’re mentioned as an afterthought compared to the benefits received from early and frequent evaluation.
11. “Tight clothes and underwire bras will make me get breast cancer.”
- Not true. Neither has any connection to breast cancer.
12. “I was told small breasts give me less of a chance of having cancer!”
- Not true. Larger breasts are sometimes more difficult to evaluate, but that’s not the same as saying the risk of cancer is increased in women with larger breasts.
13. “These lumps I have are ok because I’m breastfeeding.”
- The fact you can discover normal changes in your breast tissue doesn’t mean that all lumps discovered while breastfeeding are normal. Get evaluated.
14. “Deodorant and tanning cause breast cancer, don’t they?”
- No. Cell phones don’t either. Tanning does increase the risk of skin cancer, but that’s a topic for another day.
15. “I heard having a baby when I’m older increases my risk of breast cancer.”
- Well, not just any baby, but having one’s first baby later in life is a significant consideration. Women who give birth for the first time after age 35 are 40 percent more likely to get breast cancer than women who have their first child before age 20.
16. “Breast cancer is a death sentence.”
- Most women survive breast cancer. Give yourself the best opportunity to do so by reducing your risks, learning the principles of early detection and getting prompt treatment if ever diagnosed. We’ll focus on these considerations in the next posts.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Continuing from the earlier post with additional myths, well because you have so many questions! In fact, I’m doubling up on what you received earlier in Part I of Breast Cancer Myths.
6. “Breast cancer is preventable.”
- Unfortunately, this is not true. All of our efforts are geared toward lowering risks, early detection and effective treatment.
7. The risk of breast cancer isn’t affected by obesity.
- Not true. The risk is particularly increased in post-menopausal women with weight gain.
8. African-American women have an increased risk due to hair straighteners and relaxers.
- This myth was taken head on and debunked by the National Cancer Institute in a large 2007 study including women with significant use over a 20-year period.
9. Caffeine causes breast cancer.
- Not according to the evidence. There’s even evidence suggesting a benefit, but the data on this is just as inconclusive as that suggesting a link to breast cancer.
10. Mammograms increase breast cancer risk due to the radiation load.
- The risks of radiation are so relatively insignificant that they’re mentioned as an afterthought compared to the benefits received from early and frequent evaluation.
11. “Tight clothes and underwire bras will make me get breast cancer.”
- Not true. Neither has any connection to breast cancer.
12. “I was told small breasts give me less of a chance of having cancer!”
- Not true. Larger breasts are sometimes more difficult to evaluate, but that’s not the same as saying the risk of cancer is increased in women with larger breasts.
13. “These lumps I have are ok because I’m breastfeeding.”
- The fact you can discover normal changes in your breast tissue doesn’t mean that all lumps discovered while breastfeeding are normal. Get evaluated.
14. “Deodorant and tanning cause breast cancer, don’t they?”
- No. Cell phones don’t either. Tanning does increase the risk of skin cancer, but that’s a topic for another day.
15. “I heard having a baby when I’m older increases my risk of breast cancer.”
- Well, not just any baby, but having one’s first baby later in life is a significant consideration. Women who give birth for the first time after age 35 are 40 percent more likely to get breast cancer than women who have their first child before age 20.
16. “Breast cancer is a death sentence.”
- Most women survive breast cancer. Give yourself the best opportunity to do so by reducing your risks, learning the principles of early detection and getting prompt treatment if ever diagnosed. We’ll focus on these considerations in the next posts.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Five Myths Surrounding Breast Cancer
Before I get into the details of what you need to know about breast cancer, it’s important to clear the table of some of the persistent myths and fears that exist. The disease is tough enough as it is without the fear factor impeding our ability to fight back. Please be patient with me here. If you find these myths ridiculous, then good for you, as it indicates that you’re informed on the matter. Just understand that these are real questions that other physicians and I hear often. Remember, knowledge is power.
1. “If a family member of mine has breast cancer, that means I’ll get it too.”
- It is only true to say that women who have a family history of breast cancer have a higher risk of developing it. Overall, only approximately 10% of women diagnosed with breast cancer have a family cancer, and most women with breast cancer have no family history. In other words, a family member with breast cancer isn’t a life sentence for you, and it shouldn’t stop your efforts to lower your other risks and focus on early detection and treatment.
2. “All lumps in my breast are breast cancer.”
- There are two important points for you to remember. First, any persistent change in the breast or armpit (axilla) should not be ignored. Remember, I will be stressing the importance of early evaluation for the purposes of detection. That said, only a small percentage of breast changes represent cancer (about 80% of lumps are benign). The really good news is if you learn and perform consistent breast exams, you will detect these changes earlier than anyone else and very often early enough to make a difference.
3. “Men don’t get breast cancer.”
- Unfortunately, I know this not to be the case within my family. Annually, there are over 400 breast cancer deaths among men from over 2000 new cases being diagnosed. Men should pay attention just as women do because unfortunately, in part due to the delayed detection, the death rate of breast cancer in men is higher than in women.
4. “I heard breast implants cause cancer.”
- No. There’s no increased risk with breast implants and breast cancer. However, you can legitimately say implants sometimes obscure the view of possible cancer on a mammogram.
5. “The risk of breast cancer is always 1 in 8.”
- Actually it’s 1 in 8 during a woman’s lifetime. The important distinction is the risk increases as one ages, from 1 in 233 in a woman’s 30s up to 1 in 8 across the board by age 85.
Check back this afternoon for even more breast cancer facts and myths busted.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Before I get into the details of what you need to know about breast cancer, it’s important to clear the table of some of the persistent myths and fears that exist. The disease is tough enough as it is without the fear factor impeding our ability to fight back. Please be patient with me here. If you find these myths ridiculous, then good for you, as it indicates that you’re informed on the matter. Just understand that these are real questions that other physicians and I hear often. Remember, knowledge is power.
1. “If a family member of mine has breast cancer, that means I’ll get it too.”
- It is only true to say that women who have a family history of breast cancer have a higher risk of developing it. Overall, only approximately 10% of women diagnosed with breast cancer have a family cancer, and most women with breast cancer have no family history. In other words, a family member with breast cancer isn’t a life sentence for you, and it shouldn’t stop your efforts to lower your other risks and focus on early detection and treatment.
2. “All lumps in my breast are breast cancer.”
- There are two important points for you to remember. First, any persistent change in the breast or armpit (axilla) should not be ignored. Remember, I will be stressing the importance of early evaluation for the purposes of detection. That said, only a small percentage of breast changes represent cancer (about 80% of lumps are benign). The really good news is if you learn and perform consistent breast exams, you will detect these changes earlier than anyone else and very often early enough to make a difference.
3. “Men don’t get breast cancer.”
- Unfortunately, I know this not to be the case within my family. Annually, there are over 400 breast cancer deaths among men from over 2000 new cases being diagnosed. Men should pay attention just as women do because unfortunately, in part due to the delayed detection, the death rate of breast cancer in men is higher than in women.
4. “I heard breast implants cause cancer.”
- No. There’s no increased risk with breast implants and breast cancer. However, you can legitimately say implants sometimes obscure the view of possible cancer on a mammogram.
5. “The risk of breast cancer is always 1 in 8.”
- Actually it’s 1 in 8 during a woman’s lifetime. The important distinction is the risk increases as one ages, from 1 in 233 in a woman’s 30s up to 1 in 8 across the board by age 85.
Check back this afternoon for even more breast cancer facts and myths busted.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
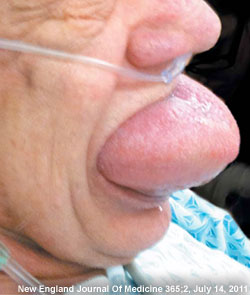
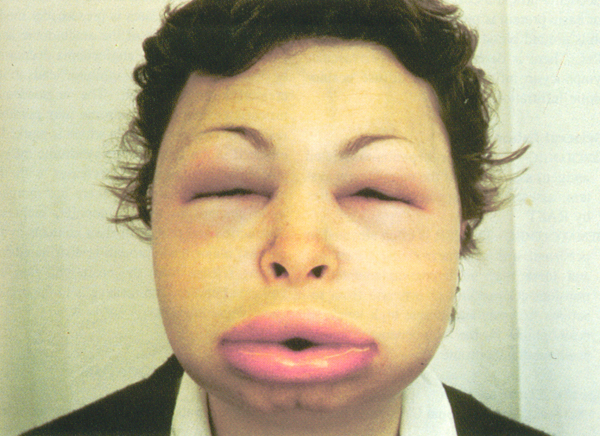
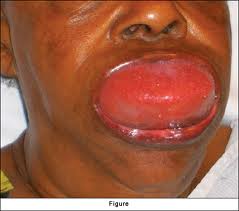
Straight, No Chaser: What Would You Do If Your Tongue Suddenly Swelled? Learn About Angioedema
Here at Straight, No Chaser, we want you to know how to prevent disease and injury because that’s a lot easier than the alternative. However, if and when the time comes, you should also have a few tools in your arsenal to stave off a life-threatening situation. One of the more scary examples of needing help is acute swelling of your tongue, sometimes so much so that your airway appears as if it will be blocked.
The most common cause of acute tongue, lip or throat swelling is called angioedema. This is an allergic reaction and occurs in two varieties.
- A life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) sometimes occurs shortly after an exposure to substance such as medicine, bee or other insect stings or food. It can throw your entire body into a state of shock, including involvement of multiple parts of the body. This can include massive tongue swelling, wheezing, low blood pressure resulting in blackouts and, of course, the rash typified by hives (urticaria).
- Sometimes lip, tongue and/or throat swelling may be the only symptoms. This is more typical of a delayed reaction to certain medications, such as types of blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers), estrogen and the class of pain medication called NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen)
With any luck, you would already know you’re at risk for this condition, and your physician may have prompted you to wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace. In these cases, your physician may have also given you medicines and instruction on how to take them in the event you feel as if your tongue is swelling and/or your throat is closing. These medicines would include epinephrine for injection, steroids and antihistamines such as Benadryl. As you dial 911 (my recommendation) or make your way to the nearest hospital, taking any or all of these medications could be life-saving. By the way, those are the among the same medicines you’ll be treated with upon arrival to the emergency room. In severe cases, you may need to be intubated (i.e. have a breathing tube placed) to maintain some opening of the airway.
If the swelling is (or assumed to be) due to any form of medication, symptoms will improve a few days after stopping it. If the swelling in this instance becomes severe enough, treatment may resemble that of the life-threatening variety.
There are few things better than cheating death. If you’re at risk, carry that injectable epinephrine (e.g. an Epi-pen). If you’re affected, take some Benadryl and/or steroids if you’ve been taught what dose to take, and most importantly, don’t wait to see if things improve. Get evaluated, get treated and get better!
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Here at Straight, No Chaser, we want you to know how to prevent disease and injury because that’s a lot easier than the alternative. However, if and when the time comes, you should also have a few tools in your arsenal to stave off a life-threatening situation. One of the more scary examples of needing help is acute swelling of your tongue, sometimes so much so that your airway appears as if it will be blocked.
The most common cause of acute tongue, lip or throat swelling is called angioedema. This is an allergic reaction and occurs in two varieties.
- A life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) sometimes occurs shortly after an exposure to substance such as medicine, bee or other insect stings or food. It can throw your entire body into a state of shock, including involvement of multiple parts of the body. This can include massive tongue swelling, wheezing, low blood pressure resulting in blackouts and, of course, the rash typified by hives (urticaria).
- Sometimes lip, tongue and/or throat swelling may be the only symptoms. This is more typical of a delayed reaction to certain medications, such as types of blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers), estrogen and the class of pain medication called NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen)
With any luck, you would already know you’re at risk for this condition, and your physician may have prompted you to wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace. In these cases, your physician may have also given you medicines and instruction on how to take them in the event you feel as if your tongue is swelling and/or your throat is closing. These medicines would include epinephrine for injection, steroids and antihistamines such as Benadryl. As you dial 911 (my recommendation) or make your way to the nearest hospital, taking any or all of these medications could be life-saving. By the way, those are the among the same medicines you’ll be treated with upon arrival to the emergency room. In severe cases, you may need to be intubated (i.e. have a breathing tube placed) to maintain some opening of the airway.
If the swelling is (or assumed to be) due to any form of medication, symptoms will improve a few days after stopping it. If the swelling in this instance becomes severe enough, treatment may resemble that of the life-threatening variety.
There are few things better than cheating death. If you’re at risk, carry that injectable epinephrine (e.g. an Epi-pen). If you’re affected, take some Benadryl and/or steroids if you’ve been taught what dose to take, and most importantly, don’t wait to see if things improve. Get evaluated, get treated and get better!
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: What Should NOT Be in Your Medicine Cabinet
Ever notice that people run straight to the medicine cabinet to do harm to themselves or others? I want you to know the harder the effort is to obtain items to hurt oneself, the less likely one is to follow through on the notion. On another related note, here’s a quick not-so-fun-but-interesting fact. One of the differences between America and say, certain European countries is the oversized influence of corporations in the States. Why am I talking about that on a medical blog? Read on. If you can’t tell where I’m going with this, you’ll get it pretty quickly.
Here’s my top five items I want you to take out your medicine cabinets and lock up.
1. Any jumbo sized container of any medication. Think about two of the most common over the counter (OTC) medications used for suicide attempts: acetaminophen (Tylenol) and salicylate (aspirin). One thing they have in common is you can buy what amounts to a tub-full of it at your local superstore in the United States. They should call these things ‘suicide quantities’, because often those in the midst of a suicide attempt will grab and swallow whatever is convenient. Many different medications will hurt you if you take enough; Tylenol and aspirin certainly fit that bill. Observing that (and additional considerations after the deaths due to the lacing of Tylenol with cyanide back in 1983), the Brits decided to not only pass a law limiting quantities, but certain medications that are high-frequency and high-risk for suicide use are now mandatorily dispensed in those annoying containers that you have to pop through the plastic container. Needless to say, observed suicide rates by medication rates plummeted as a result. Wonder why that hasn’t been implemented in the good ol’ USA?
2. Have teens in your house? Lock up the Robitussin and NyQuil. Dextromethorphan is the active ingredient in over 100 OTC cold and cough preparations. Teens use these to get high, folks. To make matters worse, they are addictive, and if taken with alcohol or other drugs, they can kill you. Then there’s ‘purple drank’ (yes, that’s how it’s spelled), in which these cough syrups containing codeine and promethazine (Benadryl) are mixed with drinks such as Sprite or Mountain Dew.
3. Have any sexual performance medications? This is part of a category of medicines called ‘medicines that can kill someone with just one pill’. That usually refers to kids or the elderly, but remember that those sexual enhancement drugs are medicines that lower your blood pressure. In the wrong person and in the wrong dose, taking such medicine – whether intentionally or accidentally – could be the last thing someone does.
3. Any narcotic. Need I say more? Remember, you do have people rummaging through your cabinets on occasion!
4. Any sharps. That includes sewing pins, needles, etc.
5. Any medication with an expiration date. The medication date actually is more of a ‘freshness’ consideration than a danger warning. However, in the wrong patient, a medicine that has less than the 100% guarantee of its needed strength that the expiration date represents could be fatal. Play it safe and get a new prescription.
There’s a lot more that could be added to this list, but I like keeping things manageable for you. Please childproof all your cabinets, and use childproof caps on your medications. I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Ever notice that people run straight to the medicine cabinet to do harm to themselves or others? I want you to know the harder the effort is to obtain items to hurt oneself, the less likely one is to follow through on the notion. On another related note, here’s a quick not-so-fun-but-interesting fact. One of the differences between America and say, certain European countries is the oversized influence of corporations in the States. Why am I talking about that on a medical blog? Read on. If you can’t tell where I’m going with this, you’ll get it pretty quickly.
Here’s my top five items I want you to take out your medicine cabinets and lock up.
1. Any jumbo sized container of any medication. Think about two of the most common over the counter (OTC) medications used for suicide attempts: acetaminophen (Tylenol) and salicylate (aspirin). One thing they have in common is you can buy what amounts to a tub-full of it at your local superstore in the United States. They should call these things ‘suicide quantities’, because often those in the midst of a suicide attempt will grab and swallow whatever is convenient. Many different medications will hurt you if you take enough; Tylenol and aspirin certainly fit that bill. Observing that (and additional considerations after the deaths due to the lacing of Tylenol with cyanide back in 1983), the Brits decided to not only pass a law limiting quantities, but certain medications that are high-frequency and high-risk for suicide use are now mandatorily dispensed in those annoying containers that you have to pop through the plastic container. Needless to say, observed suicide rates by medication rates plummeted as a result. Wonder why that hasn’t been implemented in the good ol’ USA?
2. Have teens in your house? Lock up the Robitussin and NyQuil. Dextromethorphan is the active ingredient in over 100 OTC cold and cough preparations. Teens use these to get high, folks. To make matters worse, they are addictive, and if taken with alcohol or other drugs, they can kill you. Then there’s ‘purple drank’ (yes, that’s how it’s spelled), in which these cough syrups containing codeine and promethazine (Benadryl) are mixed with drinks such as Sprite or Mountain Dew.
3. Have any sexual performance medications? This is part of a category of medicines called ‘medicines that can kill someone with just one pill’. That usually refers to kids or the elderly, but remember that those sexual enhancement drugs are medicines that lower your blood pressure. In the wrong person and in the wrong dose, taking such medicine – whether intentionally or accidentally – could be the last thing someone does.
3. Any narcotic. Need I say more? Remember, you do have people rummaging through your cabinets on occasion!
4. Any sharps. That includes sewing pins, needles, etc.
5. Any medication with an expiration date. The medication date actually is more of a ‘freshness’ consideration than a danger warning. However, in the wrong patient, a medicine that has less than the 100% guarantee of its needed strength that the expiration date represents could be fatal. Play it safe and get a new prescription.
There’s a lot more that could be added to this list, but I like keeping things manageable for you. Please childproof all your cabinets, and use childproof caps on your medications. I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: What Should Be in Your Medicine Cabinet

You’ve all done it. I’ve caught a few of you doing it. Why do you rummage through someone’s else’s medicine cabinet? Are newer homes even built with medicine cabinets anymore? Oh well… Today, I’m tackling a simple but important question in an ongoing effort to better empower you.
1. What should be in my medicine cabinet? Here’s my top five and why.
- Aspirin (324 mg). On the day you’re having a heart attack, you’ll want this available to pop in your mouth on the way to the hospital. Of all the intervention done in treating heart attacks, none is better than simply taking an aspirin. It offers a 23% reduction in mortality due to a heart attack by itself.
- Activated charcoal. This one may surprise you. Talk to your physician or pharmacist about this. If someone in your family ever overdoses on a medicine, odds are this is the first medication you’d be given in the emergency room. The sooner it’s onboard, the sooner it can begin detoxifying whatever you took. That said, there are some medications and circumstances when you shouldn’t take it, so get familiar with it by talking with your physician.
- Antiseptics such as triple antibiotic ointment for cuts, scratches and minor burns. It should be embarrassing for you to spend $1000 going to an emergency room when you could have addressed the problem at home. I guess I should include bandages here as well.
- A variety pack for colds, including antihistamines (like diphenhydramine, aka benadryl) and cough preparations. As a general rule, give yourself 3-5 days of using OTC preparations for a cold to see if it works or goes away. If not, then it’s certainly appropriate to get additional medical care. I guess I can lump a thermometer in this bullet point.
- The fifth item would be this number: 800-222-1222, which is number to the national poison control center. They will address your concerns, route you to your local poison center and help coordinate your care when you go to your emergency department.

You’ve all done it. I’ve caught a few of you doing it. Why do you rummage through someone’s else’s medicine cabinet? Are newer homes even built with medicine cabinets anymore? Oh well… Today, I’m tackling a simple but important question in an ongoing effort to better empower you.
1. What should be in my medicine cabinet? Here’s my top five and why.
- Aspirin (324 mg). On the day you’re having a heart attack, you’ll want this available to pop in your mouth on the way to the hospital. Of all the intervention done in treating heart attacks, none is better than simply taking an aspirin. It offers a 23% reduction in mortality due to a heart attack by itself.
- Activated charcoal. This one may surprise you. Talk to your physician or pharmacist about this. If someone in your family ever overdoses on a medicine, odds are this is the first medication you’d be given in the emergency room. The sooner it’s onboard, the sooner it can begin detoxifying whatever you took. That said, there are some medications and circumstances when you shouldn’t take it, so get familiar with it by talking with your physician.
- Antiseptics such as triple antibiotic ointment for cuts, scratches and minor burns. It should be embarrassing for you to spend $1000 going to an emergency room when you could have addressed the problem at home. I guess I should include bandages here as well.
- A variety pack for colds, including antihistamines (like diphenhydramine, aka benadryl) and cough preparations. As a general rule, give yourself 3-5 days of using OTC preparations for a cold to see if it works or goes away. If not, then it’s certainly appropriate to get additional medical care. I guess I can lump a thermometer in this bullet point.
- The fifth item would be this number: 800-222-1222, which is number to the national poison control center. They will address your concerns, route you to your local poison center and help coordinate your care when you go to your emergency department.
Straight, No Chaser: It's October 1st – Do You Know Where Your Affordable Care Act Health Insurance Exchanges Are? Your Top Ten Questions
No politics here folks, just facts. The bottom line is the Affordable Care Act (ACA) isn’t going anywhere prior to implementation, so let’s look at where things are. You can go here for previous comments on the ACA.
1. What changes today? The exchanges as scheduled to open for administrative business and to begin signing up customers. This is expected to affect approximately 30 million Americans who previously had not been covered by insurance plans. However, online enrollment has been delayed until November. It is still thought this won’t delay the onset of benefits.
2. Do I qualify for an exchange? You do if you are an employee of a business with less than 50 employees and have to buy your own insurance, and if you currently can’t get insurance because of a preexisting medical condition, or you can’t afford the cost.
3. So do I have insurance today if I enroll? No. Benefits begin on January 1st.
4. What about the individual mandate? It’s still in effect. Starting January 1st, most Americans must either be insured or face a fine.
5. What about the employer mandate? It’s actually been delayed until 2015. This mandate requires any company with over 50 employees to offer benefits to anyone working more than 30 hours a week.
6. Is any of this affected by the governmental shutdown? No. In short, funding for the ACA is not under the control of Congress.
7. How do I know what’s happening in my state? 16 states plus the District of Columbia are setting up their own exchanges. The other 34 states are being run either totally or partially by the federal government. Refer to the lead picture to see what your state is doing, then go to www.healthcare.gov for details.
8. How does the insurance provided by the exchanges compare with that of traditional insurance? Different exchange plans will have different levels of coverage (eg.bronze, silver, gold and platinum). You’ll get to select a plan based on your needs.
9. What about the costs? This is tricky. Obviously, the plans differ based on the one selected. Additionally, if you’re below 400% of the poverty level (which equals $45,960 for an individual and $92,200 for a family of four), you’ll be eligible for tax credits to bring down the costs of the respective plans. In general, the costs of individual insurance within the exchanges will be dramatically lower than private insurance for those who qualify.
10. Where do I sign up and/or get more information? Try www.healthcare.gov.
No politics here folks, just facts. The bottom line is the Affordable Care Act (ACA) isn’t going anywhere prior to implementation, so let’s look at where things are. You can go here for previous comments on the ACA.
1. What changes today? The exchanges as scheduled to open for administrative business and to begin signing up customers. This is expected to affect approximately 30 million Americans who previously had not been covered by insurance plans. However, online enrollment has been delayed until November. It is still thought this won’t delay the onset of benefits.
2. Do I qualify for an exchange? You do if you are an employee of a business with less than 50 employees and have to buy your own insurance, and if you currently can’t get insurance because of a preexisting medical condition, or you can’t afford the cost.
3. So do I have insurance today if I enroll? No. Benefits begin on January 1st.
4. What about the individual mandate? It’s still in effect. Starting January 1st, most Americans must either be insured or face a fine.
5. What about the employer mandate? It’s actually been delayed until 2015. This mandate requires any company with over 50 employees to offer benefits to anyone working more than 30 hours a week.
6. Is any of this affected by the governmental shutdown? No. In short, funding for the ACA is not under the control of Congress.
7. How do I know what’s happening in my state? 16 states plus the District of Columbia are setting up their own exchanges. The other 34 states are being run either totally or partially by the federal government. Refer to the lead picture to see what your state is doing, then go to www.healthcare.gov for details.
8. How does the insurance provided by the exchanges compare with that of traditional insurance? Different exchange plans will have different levels of coverage (eg.bronze, silver, gold and platinum). You’ll get to select a plan based on your needs.
9. What about the costs? This is tricky. Obviously, the plans differ based on the one selected. Additionally, if you’re below 400% of the poverty level (which equals $45,960 for an individual and $92,200 for a family of four), you’ll be eligible for tax credits to bring down the costs of the respective plans. In general, the costs of individual insurance within the exchanges will be dramatically lower than private insurance for those who qualify.
10. Where do I sign up and/or get more information? Try www.healthcare.gov.
Straight, No Chaser: Emergency Room Adventures – Trampoline Trauma

So I’m back in the emergency room with a little girl who looks like her forearm is going to fall off the rest of her upper extremity.
People love trampolines. Yet somehow the only time I seem to hear the word trampoline is when someone’s been hurt. I’m not the only one who’d vaporize them on site. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that trampolines never be used at home or in outdoor playgrounds because these injuries include head and neck contusions, fractures, strains and sprains, among other injuries.
So my patient had a (posteriorly) dislocated elbow, meaning she fell off the trampoline, landing on the back of the extended upper arm, pushing the upper arm bone (the humerus) in front of the elbow and forearm. This is how that looks.
So for the joy of bouncing on a trampoline, the child had to be put asleep so the elbow could be replaced into the appropriate position. This procedure is fraught with potential for complications, including a broken bone on the way back, as well as damage to the local nerves and arteries (brachial artery, median and ulnar nerves), which can become entrapped during the effort to relocate the bone into the elbow joint. Some limitation in fully bending the arm up and down (flexion and extension) is common after a dislocation, especially if prompt orthopedic and physical therapy follow-up isn’t obtained. This really is a high price to pay for the privilege of bouncing up and down.
So if you’re going to allow your kids to play on a trampoline, here are two tips shown to reduce injuries.
- Find one of those nets that enclose the trampoline, and make sure the frame and hooks are completely covered with padding. This is meant to protect against getting impaled, scratched or thrown from the trampoline.
- Keep the trampoline away from anything else, including trees and rocks. This works even better if the trampoline is enclosed as previously mentioned.
Think back to the little girl I had to care for and consider whether this predictable event (complete with the mental stress of being in a loud emergency room in pain, getting an IV started and being put to sleep) was worth the effort. As per routine, an ounce of prevention…
I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

So I’m back in the emergency room with a little girl who looks like her forearm is going to fall off the rest of her upper extremity.
People love trampolines. Yet somehow the only time I seem to hear the word trampoline is when someone’s been hurt. I’m not the only one who’d vaporize them on site. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that trampolines never be used at home or in outdoor playgrounds because these injuries include head and neck contusions, fractures, strains and sprains, among other injuries.
So my patient had a (posteriorly) dislocated elbow, meaning she fell off the trampoline, landing on the back of the extended upper arm, pushing the upper arm bone (the humerus) in front of the elbow and forearm. This is how that looks.
So for the joy of bouncing on a trampoline, the child had to be put asleep so the elbow could be replaced into the appropriate position. This procedure is fraught with potential for complications, including a broken bone on the way back, as well as damage to the local nerves and arteries (brachial artery, median and ulnar nerves), which can become entrapped during the effort to relocate the bone into the elbow joint. Some limitation in fully bending the arm up and down (flexion and extension) is common after a dislocation, especially if prompt orthopedic and physical therapy follow-up isn’t obtained. This really is a high price to pay for the privilege of bouncing up and down.
So if you’re going to allow your kids to play on a trampoline, here are two tips shown to reduce injuries.
- Find one of those nets that enclose the trampoline, and make sure the frame and hooks are completely covered with padding. This is meant to protect against getting impaled, scratched or thrown from the trampoline.
- Keep the trampoline away from anything else, including trees and rocks. This works even better if the trampoline is enclosed as previously mentioned.
Think back to the little girl I had to care for and consider whether this predictable event (complete with the mental stress of being in a loud emergency room in pain, getting an IV started and being put to sleep) was worth the effort. As per routine, an ounce of prevention…
I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: 10 Questions You Want Answered About Genital Herpes
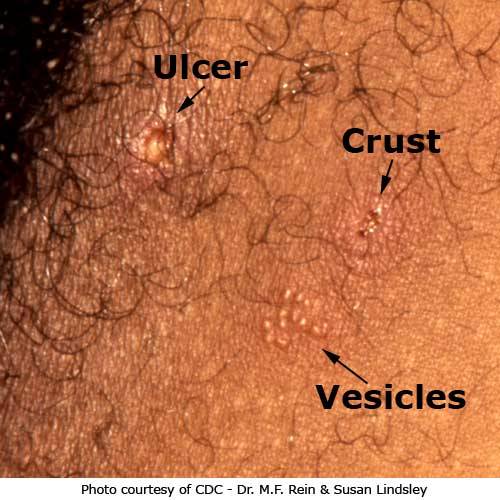
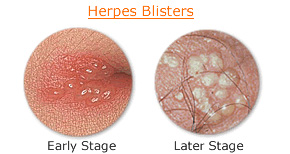
If you’re in a room, look around. Look to your left, then to your right. Look behind and in front of you. Then look deep inside yourself. Statistically, one of the people you’ve just viewed has genital herpes. Different studies suggest between 16-25% of us between ages 14-49 are infected.
Questions You Want Answered Regarding Genital Herpes
1. How common is it? That’s actually a question with two answers. One of five or six individuals have herpes (well over 50 million Americans if you’re keeping count), but it’s estimated that just short of 800,000 new cases occur every year.
2. How do you get it? Herpes is transmitted sexually (genital, oral and/or anal contact) via someone already infected.
3. Can you really get it from a cold sore? Possibly and theoretically yes, but usually not. The Herpes Simplex Virus-1 (HSV-1) is usually found in oral blisters (i.e. ‘cold sores’ or ‘fever blisters’), and its family member HSV-2 is usually found on or near the genitalia, but both can be found in either. Although the Center for Disease Control and Prevention states that “Generally, a person can only get HSV-2 infection during sexual contact with someone who has a genital HSV-2 infection,” many (if not most) emergency physicians have diagnosed herpes based on transmission from oral as well as genital sex.
4. What are the symptoms? Most have no symptoms or symptoms that may be mistaken for the flu (fever, body aches and swollen and tender lymph nodes). The prototypical symptoms are a cluster of blisters (around your genitalia, mouth, fingers or rectum) or painful ulcers.
5. Does it really stay around forever? Yes. Fortunately, the frequency and severity of outbreaks decrease as you age (assuming your immunity is good). If you are immunocompromised, HSV infections can be devastating.
6. If I catch chickenpox or shingles, does that mean I’ll have genital herpes? No. There are many different herpesviruses. HSV-2 is the virus that causes genital herpes. Varicella zoster virus (VZV) is the virus that causes chickenpox and shingles. Varicella zoster does not cause genital herpes.
7. Is it true you can catch herpes in the eye? Yes. Wash your hands. Or else…
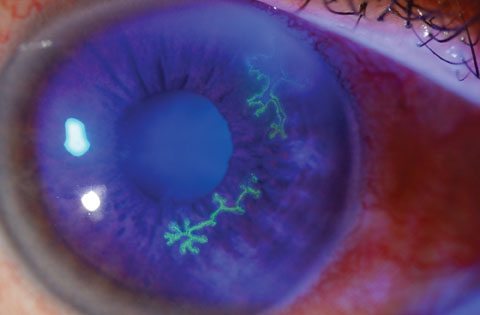
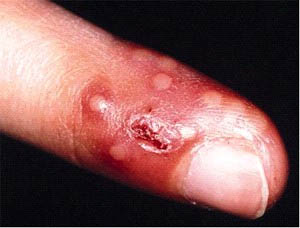
8. What was that last picture? That wasn’t an just eye, there was also a finger! Well, how did you get it got from the genitals to the eye (Please don’t answer in the comments section…)? That’s called herpetic whitlow. Notice the common theme of grouped clusters of small blisters (vesicles) again. Regarding that eye infection (herpes keratitis), it can cause blindness.
9. Is it true that women get it more often? Some estimates suggest that 25% of American women and 20% of men have genital herpes. Transmission from males to females is easier than from females to males, but guys, I wouldn’t take any chances.
10. What about the babies? 80-90% of general herpes infections to newborns are transmitted during childbirth as the newborn passes through the birth canal. C-section is recommended for all women in labor with active symptoms or lesions of herpes.
11. How do you treat this anyway? Antiviral medications are used at first sign of outbreaks. These medications don’t cure you of herpes, but they do shorten the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Plus, you’ve got to let your sexual partner know about this. It’s criminal not to.
Overall, my best advice to you is prevention, knowledge about your status, recognition of symptoms and prompt treatment. It is very important to emphasize that many people live quite normal lives with herpes. That still doesn’t mean you should be cavalier or irresponsible about it.
I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress


If you’re in a room, look around. Look to your left, then to your right. Look behind and in front of you. Then look deep inside yourself. Statistically, one of the people you’ve just viewed has genital herpes. Different studies suggest between 16-25% of us between ages 14-49 are infected.
Questions You Want Answered Regarding Genital Herpes
1. How common is it? That’s actually a question with two answers. One of five or six individuals have herpes (well over 50 million Americans if you’re keeping count), but it’s estimated that just short of 800,000 new cases occur every year.
2. How do you get it? Herpes is transmitted sexually (genital, oral and/or anal contact) via someone already infected.
3. Can you really get it from a cold sore? Possibly and theoretically yes, but usually not. The Herpes Simplex Virus-1 (HSV-1) is usually found in oral blisters (i.e. ‘cold sores’ or ‘fever blisters’), and its family member HSV-2 is usually found on or near the genitalia, but both can be found in either. Although the Center for Disease Control and Prevention states that “Generally, a person can only get HSV-2 infection during sexual contact with someone who has a genital HSV-2 infection,” many (if not most) emergency physicians have diagnosed herpes based on transmission from oral as well as genital sex.
4. What are the symptoms? Most have no symptoms or symptoms that may be mistaken for the flu (fever, body aches and swollen and tender lymph nodes). The prototypical symptoms are a cluster of blisters (around your genitalia, mouth, fingers or rectum) or painful ulcers.
5. Does it really stay around forever? Yes. Fortunately, the frequency and severity of outbreaks decrease as you age (assuming your immunity is good). If you are immunocompromised, HSV infections can be devastating.
6. If I catch chickenpox or shingles, does that mean I’ll have genital herpes? No. There are many different herpesviruses. HSV-2 is the virus that causes genital herpes. Varicella zoster virus (VZV) is the virus that causes chickenpox and shingles. Varicella zoster does not cause genital herpes.
7. Is it true you can catch herpes in the eye? Yes. Wash your hands. Or else…


8. What was that last picture? That wasn’t an just eye, there was also a finger! Well, how did you get it got from the genitals to the eye (Please don’t answer in the comments section…)? That’s called herpetic whitlow. Notice the common theme of grouped clusters of small blisters (vesicles) again. Regarding that eye infection (herpes keratitis), it can cause blindness.
9. Is it true that women get it more often? Some estimates suggest that 25% of American women and 20% of men have genital herpes. Transmission from males to females is easier than from females to males, but guys, I wouldn’t take any chances.
10. What about the babies? 80-90% of general herpes infections to newborns are transmitted during childbirth as the newborn passes through the birth canal. C-section is recommended for all women in labor with active symptoms or lesions of herpes.
11. How do you treat this anyway? Antiviral medications are used at first sign of outbreaks. These medications don’t cure you of herpes, but they do shorten the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Plus, you’ve got to let your sexual partner know about this. It’s criminal not to.
Overall, my best advice to you is prevention, knowledge about your status, recognition of symptoms and prompt treatment. It is very important to emphasize that many people live quite normal lives with herpes. That still doesn’t mean you should be cavalier or irresponsible about it.
I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Syphilis Prevention, Treatment and the Tuskegee Experience

Syphilis should be a word derived from something meaning horrible. In an earlier post, we reviewed the rather horrific progression of the symptoms of syphilis. An additionally horrible consideration is that treatment is so very easy once identified. Of course, that’s not the most horrific aspect of the disease. Read on.
Looking back retrospectively, advanced syphilis is especially disheartening because it is so easily treated and prevented. Prevention is as simple as always wearing condoms, being in a monogamous relationship with someone confirmed not to have it, checking your sexual partner prior to sex and not engaging in sex if any type of sore/ulcer is in the mouth, genitalia or anal region. Regarding treatment, syphilis once upon a time was quite the plague until penicillin was discovered; treating syphilis is how penicillin ‘made a name’ for itself. Treatment with penicillin easily kills syphilis but unfortunately does nothing for damage that has already occurred. However, as discussed in the post discussing the symptoms of syphilis, remember that treating syphilis at any point can prevent the most severe complications that lead to death. Which brings us to Tuskegee – and keep in mind this is Straight, No Chaser.
In the early 1930s, the US Public Health Service working with the Tuskegee Institute in Alabama began a study to evaluate the effectiveness of current treatments for syphilis, which at the time, were thought to be at least as bad as the disease. The study was conducted on 600 Black men, who were convinced to participate in the study with the promise of free medical exams, meals and money for burial, ‘if’ it was necessary.
The study was initially meant to last 6 months, but at some point a governmental decision was made to continue the study and observe the natural progression of syphilis until all subjects died of the disease, with a commitment obtained from the subjects that they would be autopsied ‘if’ they died. There were several problems with this decision.
- None of the patients participated under informed consent. They believed they were being treated as opposed to being observed and having medicine withheld while they were being allowed to die. In other words, the subjects were not aware of the purpose of the study.
- Penicillin was established as a true, rapidly effective treatment for syphilis and the standard of care by 1947. The study continued 25 years beyond this treatment option being available.
- Efforts by concerned individuals failed to end the study for 5 years prior to a whistleblower going to the press in 1972. The study was ended in a day.
The aftermath of the study includes the following:
- Reparations averaging a mere $15,000 per individual were given ($9M total) as well as a formal apology, delivered by President Clinton. Yep, the victims received the equivalent of $15,000 per person on average for 40 years of carrying syphilis 25 years after there was a known cure, after infecting wives and unborn children in several documented cases.
- Strict requirements for protocols for human study (i.e. Institutional Review Boards) were implemented for the first time.
It shouldn’t surprise anyone that many African-Americans remain distrustful of governmental public health efforts to this day; for many, this study continues to be the reason while vaccination isn’t optimally taken advantage of (e.g. HPV) and why organ donation rates are so relatively low in the African-American community. Even though this posture contributes to the adverse health outcomes that exist in the African-American community, it isn’t hard to see why the fear and distrust exists.
Let’s bring this full circle. When it comes to syphilis, prevention is best, and full treatment is available. At the very least, I certainly can say you’ve been warned. Folks have given their lives to make your warning possible. I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress


Syphilis should be a word derived from something meaning horrible. In an earlier post, we reviewed the rather horrific progression of the symptoms of syphilis. An additionally horrible consideration is that treatment is so very easy once identified. Of course, that’s not the most horrific aspect of the disease. Read on.
Looking back retrospectively, advanced syphilis is especially disheartening because it is so easily treated and prevented. Prevention is as simple as always wearing condoms, being in a monogamous relationship with someone confirmed not to have it, checking your sexual partner prior to sex and not engaging in sex if any type of sore/ulcer is in the mouth, genitalia or anal region. Regarding treatment, syphilis once upon a time was quite the plague until penicillin was discovered; treating syphilis is how penicillin ‘made a name’ for itself. Treatment with penicillin easily kills syphilis but unfortunately does nothing for damage that has already occurred. However, as discussed in the post discussing the symptoms of syphilis, remember that treating syphilis at any point can prevent the most severe complications that lead to death. Which brings us to Tuskegee – and keep in mind this is Straight, No Chaser.
In the early 1930s, the US Public Health Service working with the Tuskegee Institute in Alabama began a study to evaluate the effectiveness of current treatments for syphilis, which at the time, were thought to be at least as bad as the disease. The study was conducted on 600 Black men, who were convinced to participate in the study with the promise of free medical exams, meals and money for burial, ‘if’ it was necessary.
The study was initially meant to last 6 months, but at some point a governmental decision was made to continue the study and observe the natural progression of syphilis until all subjects died of the disease, with a commitment obtained from the subjects that they would be autopsied ‘if’ they died. There were several problems with this decision.
- None of the patients participated under informed consent. They believed they were being treated as opposed to being observed and having medicine withheld while they were being allowed to die. In other words, the subjects were not aware of the purpose of the study.
- Penicillin was established as a true, rapidly effective treatment for syphilis and the standard of care by 1947. The study continued 25 years beyond this treatment option being available.
- Efforts by concerned individuals failed to end the study for 5 years prior to a whistleblower going to the press in 1972. The study was ended in a day.
The aftermath of the study includes the following:
- Reparations averaging a mere $15,000 per individual were given ($9M total) as well as a formal apology, delivered by President Clinton. Yep, the victims received the equivalent of $15,000 per person on average for 40 years of carrying syphilis 25 years after there was a known cure, after infecting wives and unborn children in several documented cases.
- Strict requirements for protocols for human study (i.e. Institutional Review Boards) were implemented for the first time.
It shouldn’t surprise anyone that many African-Americans remain distrustful of governmental public health efforts to this day; for many, this study continues to be the reason while vaccination isn’t optimally taken advantage of (e.g. HPV) and why organ donation rates are so relatively low in the African-American community. Even though this posture contributes to the adverse health outcomes that exist in the African-American community, it isn’t hard to see why the fear and distrust exists.
Let’s bring this full circle. When it comes to syphilis, prevention is best, and full treatment is available. At the very least, I certainly can say you’ve been warned. Folks have given their lives to make your warning possible. I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser Editorial: The Future of Medicine – Nurses are Stepping Up to the Plate

I doubt you’ll hear this perspective anywhere else anytime soon, but there are some very interesting developments in health care underway. By way of introduction, a few decades ago, physicians abdicated the ownership and preeminent leadership role in healthcare, leaving the industry to the business minds of HMOs. During these early days, non-physician corporations actually owning medical practices and developing practice parameters were outlawed as to ensure that sufficient protections would remain in place for autonomous (and presumably honorable) medical practice.
The combination of for profit hospitals and the advent of contract medical practice management groups (particularly in emergency medicine, hospitalist medicine and radiology) combined to erode away at the corporate practice of medicine laws to where even though the laws are still on the books, suits to enforce it are now routinely defeated. Today, in addition to emergency room physicians, radiologists, surgeons, hospitalists, and anesthesiologists are more likely to be employees than owners of a practice.
In recent times, health care costs have skyrocketed to 17% of our economy, while 50 million Americans went without insurance. Meanwhile, the combination of a shortage of primary care physicians and for-profit entities’ desire to cut costs has led to the development and proliferation of alternative, less costly methods of paying individuals to provide health care. Most notably, this has included the development of advance practice nurses (e.g. nurse practitioners and nurse anesthetists – instead of family doctors and anesthesiologists). Similar interest in cost savings has led to nurses assuming senior managerial positions in hospitals instead of MBA-type executives.
It is against this backdrop that the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (aka ‘Obamacare’) passed, seeking to infuse 30 million more paying patients into the primary care arena. With ongoing physician shortages unable to meet this demand, and with there being downward cost pressure on salaries due to the goals of the ACA and desires of corporations, it’s reasonable to predict that we will see a dramatic increase in primary care nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs), which will lead to further abandonment of primary care as a physician specialty.
Meanwhile, nurses have stepped up to fill the void. In addition to the ongoing advancement of Nurse Practitioners, nurses have successfully lobbied for and created a new provider entity: ‘The Doctorate in Nursing Practice’. It is important to note that NPs and PAs can successfully treat about 85% of the things physicians routinely see. Quality concerns aside, it is an important public health consideration that additional healthcare professionals and health options are being established to fill the need of care for tens of millions of individuals more likely to use the healthcare system.
Meanwhile, regarding your doctors, a conceivable end result is physicians are being marginalized in virtually every aspect of health care. It is easy to see a future in health care 25 years from now where cost concerns have been addressed by nurses having replaced physicians in more specialties than just primary care and anesthesia, and nurses have more control of the hospital apparatus than physicians. Physicians remain oblivious to what’s happening under their noses and an insufficient interest in contributing to healthcare solutions in the ways nurses have. The Straight, No Chaser perspective is given the large segments of society that continue not to have access to care (even with implementation of the Affordable Care Act, it is estimated that 20 million American still won’t have insurance), new innovative options to address these needs are welcome and have a place in the system. What’s next is for society to ensure that this transition occurs with appropriate quality controls and public education.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

I doubt you’ll hear this perspective anywhere else anytime soon, but there are some very interesting developments in health care underway. By way of introduction, a few decades ago, physicians abdicated the ownership and preeminent leadership role in healthcare, leaving the industry to the business minds of HMOs. During these early days, non-physician corporations actually owning medical practices and developing practice parameters were outlawed as to ensure that sufficient protections would remain in place for autonomous (and presumably honorable) medical practice.
The combination of for profit hospitals and the advent of contract medical practice management groups (particularly in emergency medicine, hospitalist medicine and radiology) combined to erode away at the corporate practice of medicine laws to where even though the laws are still on the books, suits to enforce it are now routinely defeated. Today, in addition to emergency room physicians, radiologists, surgeons, hospitalists, and anesthesiologists are more likely to be employees than owners of a practice.
In recent times, health care costs have skyrocketed to 17% of our economy, while 50 million Americans went without insurance. Meanwhile, the combination of a shortage of primary care physicians and for-profit entities’ desire to cut costs has led to the development and proliferation of alternative, less costly methods of paying individuals to provide health care. Most notably, this has included the development of advance practice nurses (e.g. nurse practitioners and nurse anesthetists – instead of family doctors and anesthesiologists). Similar interest in cost savings has led to nurses assuming senior managerial positions in hospitals instead of MBA-type executives.
It is against this backdrop that the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (aka ‘Obamacare’) passed, seeking to infuse 30 million more paying patients into the primary care arena. With ongoing physician shortages unable to meet this demand, and with there being downward cost pressure on salaries due to the goals of the ACA and desires of corporations, it’s reasonable to predict that we will see a dramatic increase in primary care nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs), which will lead to further abandonment of primary care as a physician specialty.
Meanwhile, nurses have stepped up to fill the void. In addition to the ongoing advancement of Nurse Practitioners, nurses have successfully lobbied for and created a new provider entity: ‘The Doctorate in Nursing Practice’. It is important to note that NPs and PAs can successfully treat about 85% of the things physicians routinely see. Quality concerns aside, it is an important public health consideration that additional healthcare professionals and health options are being established to fill the need of care for tens of millions of individuals more likely to use the healthcare system.
Meanwhile, regarding your doctors, a conceivable end result is physicians are being marginalized in virtually every aspect of health care. It is easy to see a future in health care 25 years from now where cost concerns have been addressed by nurses having replaced physicians in more specialties than just primary care and anesthesia, and nurses have more control of the hospital apparatus than physicians. Physicians remain oblivious to what’s happening under their noses and an insufficient interest in contributing to healthcare solutions in the ways nurses have. The Straight, No Chaser perspective is given the large segments of society that continue not to have access to care (even with implementation of the Affordable Care Act, it is estimated that 20 million American still won’t have insurance), new innovative options to address these needs are welcome and have a place in the system. What’s next is for society to ensure that this transition occurs with appropriate quality controls and public education.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress