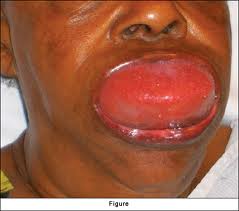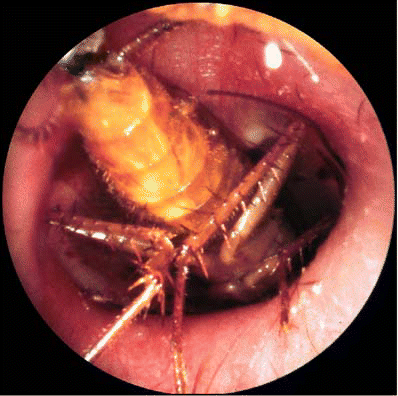
Quite a few of you had the same question after Friday’s post on objects in the ears, nose and throat:
What about insects that get in the ear, particularly when you are asleep? It’s pretty horrifying to think of some cockroach or other disgusting thing scratching around that close to your brain! What you don’t want to do is something that will irritate the critter to the point of puncturing your eardrum. Beyond freaking out, your next step should be pretty simple.
At home, consider doing what we do. If you have mineral oil, put a few drops in the ear. It’s the quickest and safest way to kill what’s in there. However, don’t delay coming to the local ER, urgent care facility or your doctor’s office. Any damage caused still needs to be evaluated.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Tag Archives: health
Straight, No Chaser: A Quick Tip for When You're Feeling Bugged…
Straight, No Chaser: That Doesn't Belong There, Little Johnny!
Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
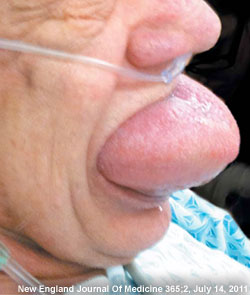
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: That Doesn't Belong There, Little Johnny
Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
Let’s talk about our kids and the things they put inside themselves. Pediatric foreign body ingestion/insertion is a common emergency room presentation. Maybe it’s just part of them exploring their world. In fact, I recall getting a pearl in my ear and a dime in my nostril as a child; maybe I wanted to start saving at a young age… Bottom line: kids get in trouble. And it’s not always their fault. Families sometimes leave things lying around the house. Children may be fed something they can’t handle. Then there’s always the older sibling putting stuff in them…
More than 100,000 cases of accidental pediatric foreign body ingestion occur each year. I’m going to address the three main orifices where things are placed and let you know the dangers, potential solutions and what to expect if and when you show up in the emergency room. Yep, three different holes, because different types of insertions occur, each with their own risks. I guess they figure if there’s a hole, something needs to go in it.
Ears:
What Happens: Kids will put anything that will fit in their ears, but the problems arise when something either gets stuck or breaks off in an ear. This can include such things as a cotton swab, food, a toy (a bead, something waxy, or something pointy) or whatever else they get their hands on. This poses a significant risk of infection, bleeding and possible rupture of the eardrum, which can lead to an entirely new set of complications.
What You Need to Know: Regardless as to the nature of the item, removal of the item is going to be very dramatic. At home, you should be very conservative in your efforts to get anything out of a child’s ear. Blind efforts may lead to pushing the item further back on the eardrum, possibly rupturing it, or jabbing it into the ear canal, causing damage and potentially setting up an infection. Such efforts usually make it even more difficult for health professionals to get at it once you come to the ER or your doctor’s office.
What happens in the ER: Drama. Depending on the size, shape and depth of the object, tools to flush it out, suck it out, scoop it out or pick it out may be used. There is no guarantee of success, and if the object is unable to be easily retrieved (without an unacceptable risk of further ear damage), the child may either be put to sleep to make the process easier, or you may be referred to an ears, nose and throat specialist.
Nose:
What Happens: Somehow kids think that because of the shape of the nostrils, round things just belong in there. Those smooth pearls, beads, marbles and kernels fit just right.
What You Need to Know: The particular danger with items placed in the nose is they can become dislodged into the airway and choke the child. You should be mindful of this as you try to get that object out yourself. One strategy that you might safely try (assuming no blood or significant pain or other apparent injury exists) is to ‘blow your child a kiss’. Put your mouth around the kids mouth and give a big puff. Sometimes this will pop the object out of the nostril! More easily, if the child is big enough to blow his/her nose, try that while occluding the unaffected nostril.
What Will Happen in the ER: We may try the same things described above. We may also use a piece of equipment called an Ambu-bag to deliver that same type of puff. If that doesn’t work, we have additional means to enter the nose and try to remove the object. The most important consideration is to protect the child’s airway.
Throat to the Stomach or Lower Airway:
What Happens and What You Need to Know: More foreign object ingestions and aspirations (passage down the airway) occur in children younger than 3 years than in other age groups, although they do occur in all ages. Even relatively immobile infants may get something inappropriate in their mouths despite not being able crawl or pick up objects and put them in the mouth. Their relative inability to chew, coupled with faster breathing rates increases the odds of objects entering the windpipe instead of the food pipe. We see simple things such as nuts, raisins, coins, magnets, seeds, foods (e.g. hot dogs and grapes), as well as toys, pins, batteries, balloons, bones and many other items. Your pediatrician has likely advised you to avoid giving certain foods until the child is at least 5 years old.
Objects that have entered or passed through the throat will leave a sensation that something is still in the throat, particularly if it scratched something on the way down. Objects in the airways run the risk of partial or complete obstruction of different parts of the airway. This can be immediately life-threatening if severe enough obstruction has occurred. There’s no guesswork here; the child will be having difficulty breathing, coughing, gasping and likely turning blue.
What Will Happen in the ER:
Management of swallowed or aspirated foreign body depends on the size of both the object and child and the object’s location.
1) If it’s in the stomach or beyond: unless there are multiple sharp objects that suggest something’s been perforated, little will be done, and you’ll be instructed to wait and watch for it in the stool.
2) If it’s in the airway, this is an emergency, and a lung specialist will need to get the object out with a special scope.
3) If it’s in the food pipe but not yet in the stomach or beyond, what’s done will depend on the size and location. Esophageal foreign bodies (that is, those in the food pipe) generally require early removal by a specialist because of their potential to cause respiratory problems (by manual pressure onto the windpipe) and complications to the esophagus itself (scratches, burns or even rupture). Most notably, ingestion of those annoying button batteries, and their lodging in the esophagus require urgent removal even if no symptoms are present because of an unacceptably high risk of complications. Sharp foreign bodies (except for single straight pins) are especially dangerous and prone to complications and most likely will also need to be removed.
So, after all that, is there any wonder why we ask you to child-proof your home? The dangers are real, and the drama of an ER visit for these things is avoidable and worth being diligent at home. Have a great, safe, healthy and happy weekend.
From the Health Library of SterlingMedicalAdvice.com: “What are some warning signs of mental illness?”
Symptoms of mental illness vary, but immediate and drastic changes in mood, thinking, and/or behaviors are common indicators. Should any such symptoms develop, seek medical attention immediately.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Symptoms of mental illness vary, but immediate and drastic changes in mood, thinking, and/or behaviors are common indicators. Should any such symptoms develop, seek medical attention immediately.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

“What should I look for as an indicator of poor mental health in children?”
Introduction
Today’s questions related to mental health in children.
“What should I look for in my child as an indicator of mental health issues?”

Today’s question is simple. The answer certainly is not. Be aware of changes in your child’s emotional, behavioral, and/or mental functioning. Remember that children often express sadness and feelings of depression in the form of anger, through outbursts, tantrums, etc. If the symptoms persist for more than a month, seek evaluation from your child’s doctor or a mental health professional. Sooner is better than later.
Follow us!
Ask your SMA expert consultant any questions you may have on this topic. Also, take the #72HoursChallenge, and join the community. Additionally, as a thank you, we’re offering you a complimentary 30-day membership at www.72hourslife.com. Just use the code #NoChaser, and yes, it’s ok if you share!
Order your copy of Dr. Sterling’s books There are 72 Hours in a Day: Using Efficiency to Better Enjoy Every Part of Your Life and The 72 Hours in a Day Workbook: The Journey to The 72 Hours Life in 72 Days at Amazon or at www.jeffreysterlingbooks.com. Another free benefit to our readers is introductory pricing with multiple orders and bundles!
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) and 844-SMA-TALK. Likewise, please share our page with your friends on WordPress! Also like us on Facebook @ SterlingMedicalAdvice.com! Follow us on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright ©2013- 2019 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Introduction
Today’s questions related to mental health in children.
“What should I look for in my child as an indicator of mental health issues?”

Today’s question is simple. The answer certainly is not. Be aware of changes in your child’s emotional, behavioral, and/or mental functioning. Remember that children often express sadness and feelings of depression in the form of anger, through outbursts, tantrums, etc. If the symptoms persist for more than a month, seek evaluation from your child’s doctor or a mental health professional. Sooner is better than later.
Follow us!
Ask your SMA expert consultant any questions you may have on this topic. Also, take the #72HoursChallenge, and join the community. Additionally, as a thank you, we’re offering you a complimentary 30-day membership at www.72hourslife.com. Just use the code #NoChaser, and yes, it’s ok if you share!
Order your copy of Dr. Sterling’s books There are 72 Hours in a Day: Using Efficiency to Better Enjoy Every Part of Your Life and The 72 Hours in a Day Workbook: The Journey to The 72 Hours Life in 72 Days at Amazon or at www.jeffreysterlingbooks.com. Another free benefit to our readers is introductory pricing with multiple orders and bundles!
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) and 844-SMA-TALK. Likewise, please share our page with your friends on WordPress! Also like us on Facebook @ SterlingMedicalAdvice.com! Follow us on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright ©2013- 2019 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Understanding Asthma – Toothpicks and Snot (Part 1 of 2)
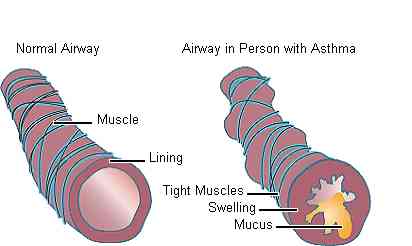
Asthma concerns me. I’ve had many close friends and family suffer with the disease. In fact, a very good friend died of an attack while in medical school, because he didn’t have his inhaler with him. In other words, this is somewhat personal. I’ve probably given more lectures on asthma than any other topic over the years, and I can say without hesitation that relative to how much we know about its prevention and treatment, I can’t think of another disease where we underperform as much as with asthma management. According to data from the National Institutes of Health, over the last few decades the death rate has increased by over 55%. The prevalence rate has increased by 75%, and among African-Americans the hospitalization rate has increased over 35%. The good news is asthma can be controlled and effectively treated. In this primer, we’ll discuss quick tips to improve the health of the asthmatic in your life.
The encouraging thing about asthma is that if you understand what causes it, you understand how to treat it. Here’s what you need to know about what causes asthma. For the purposes of discussion I am simplifying matters for general consumption.
- Asthma is a result of certain triggers, causing inflammation to your airways over a long period of time with the occurrence of attacks (intermittent exacerbations). These triggers can be thought of as allergens. Examples of these triggers include cigarette smoke, dust, aerosols, cold air, long-haired animals (especially cats), seasonal pollens, and exercise (in some).
- These triggers create a state of inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in the lungs, leading to the excessive production of mucus within the lungs’ various airway branches. If bad enough this will lead to complete obstruction of the airways. In other words you’ll stop breathing, and you will die without assistance and/or reversal.
- Exacerbations of asthma include breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing, and wheezing. Basically, because you have the functional equivalent of snot in your lungs, your airways are narrowed, and you’re having difficulty breathing. After all, it’s harder to breathe snot than air. Now imagine how your lungs feel when you’re adding cigarette smoke to that mix.
Let’s get logical. Asthma management is theoretically straightforward if you can pull it off. Prevention is treatment. I used to describe this as “Kill the Cat.” (This blog neither supports, advocates, nor is responsible for the harming of any animals resulting from this information.) In short, if you identify the triggers that precipitate your asthma attacks and then remove yourself from that environment, you will dramatically reduce, if not eliminate, your attacks. This is often described (incorrectly) in kids as “growing out of their asthma.” No one grows out of it, and you don’t cure asthma; asthmatics just stop having attacks because they’re not around the triggers.
In Part II, we discuss asthma management. In case you’re wondering, that’s where the toothpicks come in.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

Asthma concerns me. I’ve had many close friends and family suffer with the disease. In fact, a very good friend died of an attack while in medical school, because he didn’t have his inhaler with him. In other words, this is somewhat personal. I’ve probably given more lectures on asthma than any other topic over the years, and I can say without hesitation that relative to how much we know about its prevention and treatment, I can’t think of another disease where we underperform as much as with asthma management. According to data from the National Institutes of Health, over the last few decades the death rate has increased by over 55%. The prevalence rate has increased by 75%, and among African-Americans the hospitalization rate has increased over 35%. The good news is asthma can be controlled and effectively treated. In this primer, we’ll discuss quick tips to improve the health of the asthmatic in your life.
The encouraging thing about asthma is that if you understand what causes it, you understand how to treat it. Here’s what you need to know about what causes asthma. For the purposes of discussion I am simplifying matters for general consumption.
- Asthma is a result of certain triggers, causing inflammation to your airways over a long period of time with the occurrence of attacks (intermittent exacerbations). These triggers can be thought of as allergens. Examples of these triggers include cigarette smoke, dust, aerosols, cold air, long-haired animals (especially cats), seasonal pollens, and exercise (in some).
- These triggers create a state of inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in the lungs, leading to the excessive production of mucus within the lungs’ various airway branches. If bad enough this will lead to complete obstruction of the airways. In other words you’ll stop breathing, and you will die without assistance and/or reversal.
- Exacerbations of asthma include breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing, and wheezing. Basically, because you have the functional equivalent of snot in your lungs, your airways are narrowed, and you’re having difficulty breathing. After all, it’s harder to breathe snot than air. Now imagine how your lungs feel when you’re adding cigarette smoke to that mix.
Let’s get logical. Asthma management is theoretically straightforward if you can pull it off. Prevention is treatment. I used to describe this as “Kill the Cat.” (This blog neither supports, advocates, nor is responsible for the harming of any animals resulting from this information.) In short, if you identify the triggers that precipitate your asthma attacks and then remove yourself from that environment, you will dramatically reduce, if not eliminate, your attacks. This is often described (incorrectly) in kids as “growing out of their asthma.” No one grows out of it, and you don’t cure asthma; asthmatics just stop having attacks because they’re not around the triggers.
In Part II, we discuss asthma management. In case you’re wondering, that’s where the toothpicks come in.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
About www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com: How Do I Use It?

Starting November 1st, www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com will offer three separate options for your use.
- When you have a healthcare question or concern, log into www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and chat with your SMA expert consultant. Your dynamic and experienced online SMA team, representing over 15 different medical and healthcare specialties, is at your service around the clock.
- If you have a specific question on a general topic, log into www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and view the thousands of questions in our database, compiled by our expert consultants. You’ll likely find the answer you seek.
- If you desire more rounded information on a specific topic, log into www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and read the healthcare blog Straight, No Chaser. Hundreds of posts covering a wide variety of topics are available to educate and inform you.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

Starting November 1st, www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com will offer three separate options for your use.
- When you have a healthcare question or concern, log into www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and chat with your SMA expert consultant. Your dynamic and experienced online SMA team, representing over 15 different medical and healthcare specialties, is at your service around the clock.
- If you have a specific question on a general topic, log into www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and view the thousands of questions in our database, compiled by our expert consultants. You’ll likely find the answer you seek.
- If you desire more rounded information on a specific topic, log into www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and read the healthcare blog Straight, No Chaser. Hundreds of posts covering a wide variety of topics are available to educate and inform you.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
From the Health Library of SterlingMedicalAdvice.com: “Is there really a way to eat what you want and still lose weight?”
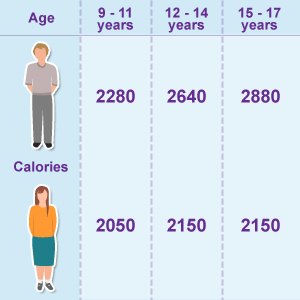
In all honesty, if you are staying within the daily calorie intake range, then yes, it’s possible. That said, foods that are bad for weight loss cause your blood sugar levels to rise and drop quickly, making you hungry. Of course, if you are craving more food, you are going to take in excessive calories and gain weight. That’s why eating nutritious foods will help you lose the weight and keep it off.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

In all honesty, if you are staying within the daily calorie intake range, then yes, it’s possible. That said, foods that are bad for weight loss cause your blood sugar levels to rise and drop quickly, making you hungry. Of course, if you are craving more food, you are going to take in excessive calories and gain weight. That’s why eating nutritious foods will help you lose the weight and keep it off.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
From the Health Library of SterlingMedicalAdvice.com: "Why Is It So Hard to Lose This 'Last' 5-10 Pounds?"
It may be that your body has reached its ‘desired’ weight – its effective, genetic set point. Reaching this level is relatively less painful than getting past it, but your body’s idea of an ‘effective’ weight won’t necessarily correspond to your personally desired level of leanness. Women in particular tend to achieve healthy homeostasis at higher body fat levels. Breaking through plateaus can be hard enough, but plateaus ordained by the body can seem to be impossible. It’s probably going to take some serious tinkering with carbs, calories, activity levels, sleep and stress. If everything else is on point and accounted for, you may be looking at healthy homeostasis (a biological balance). Then the question becomes “Do you want to mess with a good thing”. If so, stay the course; just don’t expect results as rapidly.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

It may be that your body has reached its ‘desired’ weight – its effective, genetic set point. Reaching this level is relatively less painful than getting past it, but your body’s idea of an ‘effective’ weight won’t necessarily correspond to your personally desired level of leanness. Women in particular tend to achieve healthy homeostasis at higher body fat levels. Breaking through plateaus can be hard enough, but plateaus ordained by the body can seem to be impossible. It’s probably going to take some serious tinkering with carbs, calories, activity levels, sleep and stress. If everything else is on point and accounted for, you may be looking at healthy homeostasis (a biological balance). Then the question becomes “Do you want to mess with a good thing”. If so, stay the course; just don’t expect results as rapidly.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
From the Health Library of SterlingMedicalAdvice.com: How Do I Cope?

What should I do if I’m having a hard time coping with recent changes in my life?
Adjusting to change or coping with a recent traumatic event is a difficult process and can lead to some of the same symptoms as mental illness if left unaddressed. Short-term treatment is often very effective to help prevent long-term distress, especially when you seek help sooner than later. Difficulty coping with change is normal, and talking with a professional to help make a healthy transition does not indicate you have a mental illness.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.

What should I do if I’m having a hard time coping with recent changes in my life?
Adjusting to change or coping with a recent traumatic event is a difficult process and can lead to some of the same symptoms as mental illness if left unaddressed. Short-term treatment is often very effective to help prevent long-term distress, especially when you seek help sooner than later. Difficulty coping with change is normal, and talking with a professional to help make a healthy transition does not indicate you have a mental illness.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Straight, No Chaser: Stroke Recognition
Let’s talk about strokes, aka Cerebral Vascular Accidents (CVA) and Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIA), and specifically about recognition and treatment. If you don’t remember anything else here, commit the mneumonic FAST to memory. (Details follow.)
A stroke (CVA) is an insult to some part of your brain, usually due to an inability of the blood supply to deliver needed oxygen and nutrients to that part of the brain. The brain actually approximates a “body map,” so depending on what part of your brain is affected, different parts of your body will be predictably affected. Technically, a stroke isn’t a stroke until the symptoms have been there for more than 24 hours; until then and/or if the symptoms reverse within that timeframe, the same scenario is called a TIA or a “mini-stroke.”
Think FAST, Act Faster
Here’s how the layperson can recognize a possible stroke:
- Face: Ask the affected person to show you his/her teeth (or gums). In a stroke the face often droops or is otherwise noticeably different.
- Arms: Ask the person to lift and extend the arms so the elbows are at eye level. In a stroke one side will often be weak and drift downward.
- Speech: Ask the person to say any sentence to you. In a stroke the speech will slur or otherwise be abnormal.
- Time: If any of the above occur, it’s recommended that you call 911 immediately, but if it’s my family, I’m getting in a car and going to the nearest MAJOR medical center—not the nearest hospital, which is where the ambulance will take you. There are important differences in hospitals when it comes to stroke treatment (which you won’t know offhand), because some are designated stroke centers and others are not. Friends, this is not the situation where you should wait hours or overnight to see if things get better. Time is (brain) tissue.
It is VERY important that you act on any of the above symptoms (F-A-S) within three (3) hours of symptom onset. Important treatment options are available within the first four and a half (4 ½) hours that are otherwise unavailable.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Let’s talk about strokes, aka Cerebral Vascular Accidents (CVA) and Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIA), and specifically about recognition and treatment. If you don’t remember anything else here, commit the mneumonic FAST to memory. (Details follow.)
A stroke (CVA) is an insult to some part of your brain, usually due to an inability of the blood supply to deliver needed oxygen and nutrients to that part of the brain. The brain actually approximates a “body map,” so depending on what part of your brain is affected, different parts of your body will be predictably affected. Technically, a stroke isn’t a stroke until the symptoms have been there for more than 24 hours; until then and/or if the symptoms reverse within that timeframe, the same scenario is called a TIA or a “mini-stroke.”
Think FAST, Act Faster
Here’s how the layperson can recognize a possible stroke:
- Face: Ask the affected person to show you his/her teeth (or gums). In a stroke the face often droops or is otherwise noticeably different.
- Arms: Ask the person to lift and extend the arms so the elbows are at eye level. In a stroke one side will often be weak and drift downward.
- Speech: Ask the person to say any sentence to you. In a stroke the speech will slur or otherwise be abnormal.
- Time: If any of the above occur, it’s recommended that you call 911 immediately, but if it’s my family, I’m getting in a car and going to the nearest MAJOR medical center—not the nearest hospital, which is where the ambulance will take you. There are important differences in hospitals when it comes to stroke treatment (which you won’t know offhand), because some are designated stroke centers and others are not. Friends, this is not the situation where you should wait hours or overnight to see if things get better. Time is (brain) tissue.
It is VERY important that you act on any of the above symptoms (F-A-S) within three (3) hours of symptom onset. Important treatment options are available within the first four and a half (4 ½) hours that are otherwise unavailable.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) will offer beginning November 1. Until then enjoy some our favorite posts and frequently asked questions as well as a daily note explaining the benefits of SMA membership. Please share our page with your Friends on WordPress, and we can be found on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and on Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Signs, Symptoms and Prognosis of Breast Cancer
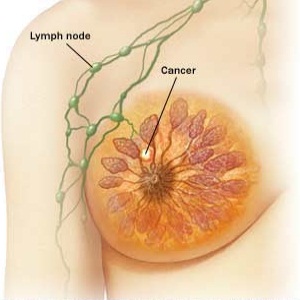
So, after all we’ve discussed this week, this is what it comes down to: the one in eight lifetime risk has landed at your doorstep. What happens next is very important. The ability to recognize and obtain early treatment for breast cancer (or not) will determine the length and quality of the rest of your life. Remember, most women survive breast cancer; there are approximately 3 million breast cancer survivors in the U.S. That said, also remember that there are about 40,000 annual deaths from breast cancer. The combination of breast self-exams and widespread use of screening mammograms has increased the number of breast cancers found before they cause any symptoms. Unfortunately, many others go undetected because of the limitations or failure to engage those two modalities.
I really want you to become familiar with your bodies (in this instance, your breasts). The most common symptom of breast cancer is a new lump, but you should be in tune with any new change or irregularity, including pain, swelling, redness, irritation, nipple inversion or other irregularity. Remember, breast tissue extends into the armpit (axilla), and you may find swollen and tender lymph nodes in the axilla or near the collarbone (clavicle). My bottom line: you be responsible for diligently assessing any abnormalities, and your healthcare team will determine the cause and if it’s cancer.
One more pitch for early detection: if breast cancer is detected prior to spread to the lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate (with appropriate treatment) is as high as 98%. If it’s reached the lymph nodes, that drops to approximately 84%, and if it has spread to other body parts (e.g. the lungs, liver and bone – this is called metastatic cancer or carcinoma), the average 5-year survival rate drops to 23%.
This represents a drop in mortality rates by about 25% since 1990. Unfortunately, survivors must live with the uncertainties of possible recurrent cancer and some risk for complications from the treatment itself. That said, recurrences of cancer usually develop within 5 years of treatment. About 25% of recurrences and 50% of new cancers in the opposite breast occur after 5 years.
Many of you have asked about tumor ‘predictors’. I’ll end this post with a look at three considerations, although there are many others:
1. Breast cancer cells may contain binding sites for hormones (estrogen and progesterone). When that’s the case, these cells are called hormone receptor-positive; if not, they’re called hormone receptor negative. When cancer cells are hormone receptor positive, they are responsive to certain medications (such as tamoxifen and others). This improves prognosis. These types of cells also happen to grow more slowly, which also helps. On the other hand, hormone receptor-negative cells only respond to chemotherapy.
2. Tumor markers are proteins released from cancer cells that are able to be identified during the disease. They are notable for demonstrating (or predicting) how aggressive one’s cancer may be. The one I will mention (yes, there are others) is the HER2 marker, which is especially quick-growing and aggressive. The American Cancer Society recommends all newly diagnosed women be tested for this. Fortunately, only 20% women with invasive breast cancer are positive for HER2.
3. Curiously, tumor location within the breast has proven to be an important predictor. Tumors in the middle of the breast are most serious than those toward the outside.
I wish all of you breast cancer survivors or those with family members affected all the best with this. I hope these posts have again pointed out the importance of lowering your risk profile and early detection and treatment. This is another illustration of the shortcomings of our typical approach to health care; relying on medical care is not the same as comprehensive healthcare. The time to engage the fight against breast cancer is not in the midst of advanced disease.
I welcome your comments or questions.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
I really want you to become familiar with your bodies (in this instance, your breasts). The most common symptom of breast cancer is a new lump, but you should be in tune with any new change or irregularity, including pain, swelling, redness, irritation, nipple inversion or other irregularity. Remember, breast tissue extends into the armpit (axilla), and you may find swollen and tender lymph nodes in the axilla or near the collarbone (clavicle). My bottom line: you be responsible for diligently assessing any abnormalities, and your healthcare team will determine the cause and if it’s cancer.
One more pitch for early detection: if breast cancer is detected prior to spread to the lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate (with appropriate treatment) is as high as 98%. If it’s reached the lymph nodes, that drops to approximately 84%, and if it has spread to other body parts (e.g. the lungs, liver and bone – this is called metastatic cancer or carcinoma), the average 5-year survival rate drops to 23%.
This represents a drop in mortality rates by about 25% since 1990. Unfortunately, survivors must live with the uncertainties of possible recurrent cancer and some risk for complications from the treatment itself. That said, recurrences of cancer usually develop within 5 years of treatment. About 25% of recurrences and 50% of new cancers in the opposite breast occur after 5 years.
Many of you have asked about tumor ‘predictors’. I’ll end this post with a look at three considerations, although there are many others:
1. Breast cancer cells may contain binding sites for hormones (estrogen and progesterone). When that’s the case, these cells are called hormone receptor-positive; if not, they’re called hormone receptor negative. When cancer cells are hormone receptor positive, they are responsive to certain medications (such as tamoxifen and others). This improves prognosis. These types of cells also happen to grow more slowly, which also helps. On the other hand, hormone receptor-negative cells only respond to chemotherapy.
2. Tumor markers are proteins released from cancer cells that are able to be identified during the disease. They are notable for demonstrating (or predicting) how aggressive one’s cancer may be. The one I will mention (yes, there are others) is the HER2 marker, which is especially quick-growing and aggressive. The American Cancer Society recommends all newly diagnosed women be tested for this. Fortunately, only 20% women with invasive breast cancer are positive for HER2.
3. Curiously, tumor location within the breast has proven to be an important predictor. Tumors in the middle of the breast are most serious than those toward the outside.
I wish all of you breast cancer survivors or those with family members affected all the best with this. I hope these posts have again pointed out the importance of lowering your risk profile and early detection and treatment. This is another illustration of the shortcomings of our typical approach to health care; relying on medical care is not the same as comprehensive healthcare. The time to engage the fight against breast cancer is not in the midst of advanced disease.
I welcome your comments or questions.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: The Reach of Breast Cancer and Your Risk Factors
Even as a physician, I am left to think about the horror of being a woman with a lifetime risk of acquiring breast cancer that’s 1 in 8. The only thing I can think of off-hand and relate to similarly is the risk for trauma being an inner-city minority kid. This risk of breast cancer is compounded by the reality that there is no way to prevent it. Thus, it must be emphasized early and often: risk factor identification and reduction, coupled with early evaluation, detection and treatment are absolutely vital.
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer contracted by American women (after skin cancer), and it is the second most common cause of death from cancer (after lung cancer). More than a quarter of a million new cases will be diagnosed in women yearly, and approximately 40,000 women will die from complications of breast cancer annually (that’s over 100 deaths every day).
In the event the previous information seemed like too much gloom and doom, understand that the tide has been stemmed. After more than two decades of increase, rates of new cases of breast cancer began dropping in 2000 and have stabilized. This is largely thought to be due to declining rates of post-menopausal hormone use in response to results from major research projects. As you may know, such hormone use has been shown to increase the risk of both breast cancer and heart disease.
Speaking of risks, I don’t especially like this part of the conversation because it always comes across as if everything is a risk factor, and there are still controversies about what is or isn’t a risk. As a result, patients end up confused and paralyzed into inaction. Therefore, I’ll mention just enough for you to understand and work with; if you have specific questions on what you’ve heard that I haven’t already addressed in the breast cancer myth posts (Parts I and II), feel free to ask.
There are risk factors you can’t change, like aging, family history and being a woman. Having these risk factors simply means you need to be more diligent in performing self exams and seeking early care for suspicious findings. Now, there are other risk factors you can minimize. Oral contraceptive use, postmenopausal hormonal therapy, choosing not to breast feed, alcohol use and obesity are all risk factors for breast cancer that are under your control.
The bottom line is your risk factors don’t cause cancer, and the absence of risk factors doesn’t ensure you won’t have breast cancer. For example, men contract breast cancer as well. What it all comes down to is you must be diligent in performing exams and getting evaluated and treated if something abnormal is discovered. We’ll discuss some of that next.
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer contracted by American women (after skin cancer), and it is the second most common cause of death from cancer (after lung cancer). More than a quarter of a million new cases will be diagnosed in women yearly, and approximately 40,000 women will die from complications of breast cancer annually (that’s over 100 deaths every day).
In the event the previous information seemed like too much gloom and doom, understand that the tide has been stemmed. After more than two decades of increase, rates of new cases of breast cancer began dropping in 2000 and have stabilized. This is largely thought to be due to declining rates of post-menopausal hormone use in response to results from major research projects. As you may know, such hormone use has been shown to increase the risk of both breast cancer and heart disease.
Speaking of risks, I don’t especially like this part of the conversation because it always comes across as if everything is a risk factor, and there are still controversies about what is or isn’t a risk. As a result, patients end up confused and paralyzed into inaction. Therefore, I’ll mention just enough for you to understand and work with; if you have specific questions on what you’ve heard that I haven’t already addressed in the breast cancer myth posts (Parts I and II), feel free to ask.
There are risk factors you can’t change, like aging, family history and being a woman. Having these risk factors simply means you need to be more diligent in performing self exams and seeking early care for suspicious findings. Now, there are other risk factors you can minimize. Oral contraceptive use, postmenopausal hormonal therapy, choosing not to breast feed, alcohol use and obesity are all risk factors for breast cancer that are under your control.
The bottom line is your risk factors don’t cause cancer, and the absence of risk factors doesn’t ensure you won’t have breast cancer. For example, men contract breast cancer as well. What it all comes down to is you must be diligent in performing exams and getting evaluated and treated if something abnormal is discovered. We’ll discuss some of that next.
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: (El)even More Myths Regarding Breast Cancer
Continuing from the earlier post with additional myths, well because you have so many questions! In fact, I’m doubling up on what you received earlier in Part I of Breast Cancer Myths.
6. “Breast cancer is preventable.”
- Unfortunately, this is not true. All of our efforts are geared toward lowering risks, early detection and effective treatment.
7. The risk of breast cancer isn’t affected by obesity.
- Not true. The risk is particularly increased in post-menopausal women with weight gain.
8. African-American women have an increased risk due to hair straighteners and relaxers.
- This myth was taken head on and debunked by the National Cancer Institute in a large 2007 study including women with significant use over a 20-year period.
9. Caffeine causes breast cancer.
- Not according to the evidence. There’s even evidence suggesting a benefit, but the data on this is just as inconclusive as that suggesting a link to breast cancer.
10. Mammograms increase breast cancer risk due to the radiation load.
- The risks of radiation are so relatively insignificant that they’re mentioned as an afterthought compared to the benefits received from early and frequent evaluation.
11. “Tight clothes and underwire bras will make me get breast cancer.”
- Not true. Neither has any connection to breast cancer.
12. “I was told small breasts give me less of a chance of having cancer!”
- Not true. Larger breasts are sometimes more difficult to evaluate, but that’s not the same as saying the risk of cancer is increased in women with larger breasts.
13. “These lumps I have are ok because I’m breastfeeding.”
- The fact you can discover normal changes in your breast tissue doesn’t mean that all lumps discovered while breastfeeding are normal. Get evaluated.
14. “Deodorant and tanning cause breast cancer, don’t they?”
- No. Cell phones don’t either. Tanning does increase the risk of skin cancer, but that’s a topic for another day.
15. “I heard having a baby when I’m older increases my risk of breast cancer.”
- Well, not just any baby, but having one’s first baby later in life is a significant consideration. Women who give birth for the first time after age 35 are 40 percent more likely to get breast cancer than women who have their first child before age 20.
16. “Breast cancer is a death sentence.”
- Most women survive breast cancer. Give yourself the best opportunity to do so by reducing your risks, learning the principles of early detection and getting prompt treatment if ever diagnosed. We’ll focus on these considerations in the next posts.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Continuing from the earlier post with additional myths, well because you have so many questions! In fact, I’m doubling up on what you received earlier in Part I of Breast Cancer Myths.
6. “Breast cancer is preventable.”
- Unfortunately, this is not true. All of our efforts are geared toward lowering risks, early detection and effective treatment.
7. The risk of breast cancer isn’t affected by obesity.
- Not true. The risk is particularly increased in post-menopausal women with weight gain.
8. African-American women have an increased risk due to hair straighteners and relaxers.
- This myth was taken head on and debunked by the National Cancer Institute in a large 2007 study including women with significant use over a 20-year period.
9. Caffeine causes breast cancer.
- Not according to the evidence. There’s even evidence suggesting a benefit, but the data on this is just as inconclusive as that suggesting a link to breast cancer.
10. Mammograms increase breast cancer risk due to the radiation load.
- The risks of radiation are so relatively insignificant that they’re mentioned as an afterthought compared to the benefits received from early and frequent evaluation.
11. “Tight clothes and underwire bras will make me get breast cancer.”
- Not true. Neither has any connection to breast cancer.
12. “I was told small breasts give me less of a chance of having cancer!”
- Not true. Larger breasts are sometimes more difficult to evaluate, but that’s not the same as saying the risk of cancer is increased in women with larger breasts.
13. “These lumps I have are ok because I’m breastfeeding.”
- The fact you can discover normal changes in your breast tissue doesn’t mean that all lumps discovered while breastfeeding are normal. Get evaluated.
14. “Deodorant and tanning cause breast cancer, don’t they?”
- No. Cell phones don’t either. Tanning does increase the risk of skin cancer, but that’s a topic for another day.
15. “I heard having a baby when I’m older increases my risk of breast cancer.”
- Well, not just any baby, but having one’s first baby later in life is a significant consideration. Women who give birth for the first time after age 35 are 40 percent more likely to get breast cancer than women who have their first child before age 20.
16. “Breast cancer is a death sentence.”
- Most women survive breast cancer. Give yourself the best opportunity to do so by reducing your risks, learning the principles of early detection and getting prompt treatment if ever diagnosed. We’ll focus on these considerations in the next posts.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Five Myths Surrounding Breast Cancer
Before I get into the details of what you need to know about breast cancer, it’s important to clear the table of some of the persistent myths and fears that exist. The disease is tough enough as it is without the fear factor impeding our ability to fight back. Please be patient with me here. If you find these myths ridiculous, then good for you, as it indicates that you’re informed on the matter. Just understand that these are real questions that other physicians and I hear often. Remember, knowledge is power.
1. “If a family member of mine has breast cancer, that means I’ll get it too.”
- It is only true to say that women who have a family history of breast cancer have a higher risk of developing it. Overall, only approximately 10% of women diagnosed with breast cancer have a family cancer, and most women with breast cancer have no family history. In other words, a family member with breast cancer isn’t a life sentence for you, and it shouldn’t stop your efforts to lower your other risks and focus on early detection and treatment.
2. “All lumps in my breast are breast cancer.”
- There are two important points for you to remember. First, any persistent change in the breast or armpit (axilla) should not be ignored. Remember, I will be stressing the importance of early evaluation for the purposes of detection. That said, only a small percentage of breast changes represent cancer (about 80% of lumps are benign). The really good news is if you learn and perform consistent breast exams, you will detect these changes earlier than anyone else and very often early enough to make a difference.
3. “Men don’t get breast cancer.”
- Unfortunately, I know this not to be the case within my family. Annually, there are over 400 breast cancer deaths among men from over 2000 new cases being diagnosed. Men should pay attention just as women do because unfortunately, in part due to the delayed detection, the death rate of breast cancer in men is higher than in women.
4. “I heard breast implants cause cancer.”
- No. There’s no increased risk with breast implants and breast cancer. However, you can legitimately say implants sometimes obscure the view of possible cancer on a mammogram.
5. “The risk of breast cancer is always 1 in 8.”
- Actually it’s 1 in 8 during a woman’s lifetime. The important distinction is the risk increases as one ages, from 1 in 233 in a woman’s 30s up to 1 in 8 across the board by age 85.
Check back this afternoon for even more breast cancer facts and myths busted.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Before I get into the details of what you need to know about breast cancer, it’s important to clear the table of some of the persistent myths and fears that exist. The disease is tough enough as it is without the fear factor impeding our ability to fight back. Please be patient with me here. If you find these myths ridiculous, then good for you, as it indicates that you’re informed on the matter. Just understand that these are real questions that other physicians and I hear often. Remember, knowledge is power.
1. “If a family member of mine has breast cancer, that means I’ll get it too.”
- It is only true to say that women who have a family history of breast cancer have a higher risk of developing it. Overall, only approximately 10% of women diagnosed with breast cancer have a family cancer, and most women with breast cancer have no family history. In other words, a family member with breast cancer isn’t a life sentence for you, and it shouldn’t stop your efforts to lower your other risks and focus on early detection and treatment.
2. “All lumps in my breast are breast cancer.”
- There are two important points for you to remember. First, any persistent change in the breast or armpit (axilla) should not be ignored. Remember, I will be stressing the importance of early evaluation for the purposes of detection. That said, only a small percentage of breast changes represent cancer (about 80% of lumps are benign). The really good news is if you learn and perform consistent breast exams, you will detect these changes earlier than anyone else and very often early enough to make a difference.
3. “Men don’t get breast cancer.”
- Unfortunately, I know this not to be the case within my family. Annually, there are over 400 breast cancer deaths among men from over 2000 new cases being diagnosed. Men should pay attention just as women do because unfortunately, in part due to the delayed detection, the death rate of breast cancer in men is higher than in women.
4. “I heard breast implants cause cancer.”
- No. There’s no increased risk with breast implants and breast cancer. However, you can legitimately say implants sometimes obscure the view of possible cancer on a mammogram.
5. “The risk of breast cancer is always 1 in 8.”
- Actually it’s 1 in 8 during a woman’s lifetime. The important distinction is the risk increases as one ages, from 1 in 233 in a woman’s 30s up to 1 in 8 across the board by age 85.
Check back this afternoon for even more breast cancer facts and myths busted.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month

Breast cancer disturbs me deeply, and if it doesn’t affect you as well, you haven’t been paying attention. One in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime. It’s more likely than not that every single one of us has been affected by this, either directly or through a friend or family member.
Breast cancer is different. We’ve found the way to eradicate certain cancers and have made remarkable progress on others. Aside from the hereditary component, breast cancer seems so…random, so dehumanizing and so debilitating to so many. Unlike so many of the things I address as an emergency physician, breast cancer isn’t like trauma, STDs and many other conditions, where one is often directly suffering the consequences of their behavior. It is vital that you appreciate the need and value for early detection to give yourself the best possible chance for the best possible outcomes. I’ll be discussing all these considerations in detail throughout the week.
I appreciate the sentiment behind a National Breast Cancer Awareness Month, but if I could offer you anything on this, it would be a plea to be ‘aware’ every month, and use this month as a (re)commitment to take basic steps that will reduce your risk, a charge to maintain steps for early evaluation and a prod to point you toward prompt treatment if and when needed. In fact, those three areas will be the topics of my next few posts. In the meantime, please share this or other information about breast cancer to any and all females in your life. I also hope you choose to engage your family, friends and others in conversations geared to improving breast cancer awareness. Odds are many of them have been or will be affected by breast cancer.
I welcome your comments or questions.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

Breast cancer disturbs me deeply, and if it doesn’t affect you as well, you haven’t been paying attention. One in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime. It’s more likely than not that every single one of us has been affected by this, either directly or through a friend or family member.
Breast cancer is different. We’ve found the way to eradicate certain cancers and have made remarkable progress on others. Aside from the hereditary component, breast cancer seems so…random, so dehumanizing and so debilitating to so many. Unlike so many of the things I address as an emergency physician, breast cancer isn’t like trauma, STDs and many other conditions, where one is often directly suffering the consequences of their behavior. It is vital that you appreciate the need and value for early detection to give yourself the best possible chance for the best possible outcomes. I’ll be discussing all these considerations in detail throughout the week.
I appreciate the sentiment behind a National Breast Cancer Awareness Month, but if I could offer you anything on this, it would be a plea to be ‘aware’ every month, and use this month as a (re)commitment to take basic steps that will reduce your risk, a charge to maintain steps for early evaluation and a prod to point you toward prompt treatment if and when needed. In fact, those three areas will be the topics of my next few posts. In the meantime, please share this or other information about breast cancer to any and all females in your life. I also hope you choose to engage your family, friends and others in conversations geared to improving breast cancer awareness. Odds are many of them have been or will be affected by breast cancer.
I welcome your comments or questions.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: What Would You Do If Your Tongue Suddenly Swelled? Learn About Angioedema
Here at Straight, No Chaser, we want you to know how to prevent disease and injury because that’s a lot easier than the alternative. However, if and when the time comes, you should also have a few tools in your arsenal to stave off a life-threatening situation. One of the more scary examples of needing help is acute swelling of your tongue, sometimes so much so that your airway appears as if it will be blocked.
The most common cause of acute tongue, lip or throat swelling is called angioedema. This is an allergic reaction and occurs in two varieties.
- A life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) sometimes occurs shortly after an exposure to substance such as medicine, bee or other insect stings or food. It can throw your entire body into a state of shock, including involvement of multiple parts of the body. This can include massive tongue swelling, wheezing, low blood pressure resulting in blackouts and, of course, the rash typified by hives (urticaria).
- Sometimes lip, tongue and/or throat swelling may be the only symptoms. This is more typical of a delayed reaction to certain medications, such as types of blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers), estrogen and the class of pain medication called NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen)
With any luck, you would already know you’re at risk for this condition, and your physician may have prompted you to wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace. In these cases, your physician may have also given you medicines and instruction on how to take them in the event you feel as if your tongue is swelling and/or your throat is closing. These medicines would include epinephrine for injection, steroids and antihistamines such as Benadryl. As you dial 911 (my recommendation) or make your way to the nearest hospital, taking any or all of these medications could be life-saving. By the way, those are the among the same medicines you’ll be treated with upon arrival to the emergency room. In severe cases, you may need to be intubated (i.e. have a breathing tube placed) to maintain some opening of the airway.
If the swelling is (or assumed to be) due to any form of medication, symptoms will improve a few days after stopping it. If the swelling in this instance becomes severe enough, treatment may resemble that of the life-threatening variety.
There are few things better than cheating death. If you’re at risk, carry that injectable epinephrine (e.g. an Epi-pen). If you’re affected, take some Benadryl and/or steroids if you’ve been taught what dose to take, and most importantly, don’t wait to see if things improve. Get evaluated, get treated and get better!
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Here at Straight, No Chaser, we want you to know how to prevent disease and injury because that’s a lot easier than the alternative. However, if and when the time comes, you should also have a few tools in your arsenal to stave off a life-threatening situation. One of the more scary examples of needing help is acute swelling of your tongue, sometimes so much so that your airway appears as if it will be blocked.
The most common cause of acute tongue, lip or throat swelling is called angioedema. This is an allergic reaction and occurs in two varieties.
- A life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) sometimes occurs shortly after an exposure to substance such as medicine, bee or other insect stings or food. It can throw your entire body into a state of shock, including involvement of multiple parts of the body. This can include massive tongue swelling, wheezing, low blood pressure resulting in blackouts and, of course, the rash typified by hives (urticaria).
- Sometimes lip, tongue and/or throat swelling may be the only symptoms. This is more typical of a delayed reaction to certain medications, such as types of blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers), estrogen and the class of pain medication called NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen)
With any luck, you would already know you’re at risk for this condition, and your physician may have prompted you to wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace. In these cases, your physician may have also given you medicines and instruction on how to take them in the event you feel as if your tongue is swelling and/or your throat is closing. These medicines would include epinephrine for injection, steroids and antihistamines such as Benadryl. As you dial 911 (my recommendation) or make your way to the nearest hospital, taking any or all of these medications could be life-saving. By the way, those are the among the same medicines you’ll be treated with upon arrival to the emergency room. In severe cases, you may need to be intubated (i.e. have a breathing tube placed) to maintain some opening of the airway.
If the swelling is (or assumed to be) due to any form of medication, symptoms will improve a few days after stopping it. If the swelling in this instance becomes severe enough, treatment may resemble that of the life-threatening variety.
There are few things better than cheating death. If you’re at risk, carry that injectable epinephrine (e.g. an Epi-pen). If you’re affected, take some Benadryl and/or steroids if you’ve been taught what dose to take, and most importantly, don’t wait to see if things improve. Get evaluated, get treated and get better!
I welcome your questions and comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: Five Important Questions About Contact Lenses
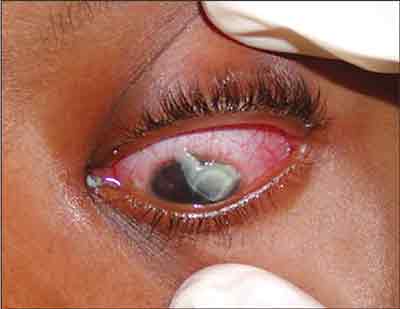
Question: Which is better: disposable or regular contact lenses?
The development of disposable contact lenses has lessened the risk of various eye problems. This isn’t the same as saying regular lenses aren’t good or even just as good. Daily use (i.e. disposable) contacts don’t require cleaning solutions, which were commonly used for contacts in the past to increase the longevity of them. When you’re next ready for lenses, ask about silicon hydrogel lens. Evidence suggests they are even better for comfort and lower risk for eye problems.
Question: Can I wear my contact lenses when I go swimming?
You can, but you shouldn’t, according to the FDA (Food and Drug Administration). Swimming can cause absorption of chemicals (including chlorine) and bacteria from the water, leading to an eye infection. Additionally, contacts can adhere to the eye after swimming. This can lead to ulceration of parts of the eye (e.g. cornea).
Question: Can I wear my contact lenses while I sleep?
You can use extended wear contacts while you sleep if this has been approved in advance by your optometrist or ophthalmologist; they can be used for up to seven days if recommended as such. Daily wear contacts must be removed prior to sleep – even a nap.
Question: What steps help prevent fungal infections caused by contact lenses?
First, you should understand your risks, which include prior eye damage or a diminished immune system. Fungal infections are a particular concern for those wearing soft contact lens with risk factors. To reduce your risk, be sure to thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water. Be especially careful to avoid lint on your hands before handling your contacts. Avoid extending the use of your contact lens beyond the recommendations of your eye provider. Be sure to keep your lens case clean, and replace the case every 3-6 months. In the unlikely event you’re still using Bausch & Lomb ReNu ® with MoistureLoc® Multi-Purpose Solution, discard it. It’s been recalled due to an increase rate of eye fungal infections.
Question: How do I know if my contact lenses have caused an eye infection?
Be on the lookout for redness, swelling, tearing and/or eye discharge, light sensitivity, blurred vision and pain that doesn’t improve after removal of the contacts. If you have symptoms like this, remove the contacts and get medical assistance.
Remember to pause before inserting anything in your eyes. The consequences of bad decisions can be devastating and irreversible. I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress

Question: Which is better: disposable or regular contact lenses?
The development of disposable contact lenses has lessened the risk of various eye problems. This isn’t the same as saying regular lenses aren’t good or even just as good. Daily use (i.e. disposable) contacts don’t require cleaning solutions, which were commonly used for contacts in the past to increase the longevity of them. When you’re next ready for lenses, ask about silicon hydrogel lens. Evidence suggests they are even better for comfort and lower risk for eye problems.
Question: Can I wear my contact lenses when I go swimming?
You can, but you shouldn’t, according to the FDA (Food and Drug Administration). Swimming can cause absorption of chemicals (including chlorine) and bacteria from the water, leading to an eye infection. Additionally, contacts can adhere to the eye after swimming. This can lead to ulceration of parts of the eye (e.g. cornea).
Question: Can I wear my contact lenses while I sleep?
You can use extended wear contacts while you sleep if this has been approved in advance by your optometrist or ophthalmologist; they can be used for up to seven days if recommended as such. Daily wear contacts must be removed prior to sleep – even a nap.
Question: What steps help prevent fungal infections caused by contact lenses?
First, you should understand your risks, which include prior eye damage or a diminished immune system. Fungal infections are a particular concern for those wearing soft contact lens with risk factors. To reduce your risk, be sure to thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water. Be especially careful to avoid lint on your hands before handling your contacts. Avoid extending the use of your contact lens beyond the recommendations of your eye provider. Be sure to keep your lens case clean, and replace the case every 3-6 months. In the unlikely event you’re still using Bausch & Lomb ReNu ® with MoistureLoc® Multi-Purpose Solution, discard it. It’s been recalled due to an increase rate of eye fungal infections.
Question: How do I know if my contact lenses have caused an eye infection?
Be on the lookout for redness, swelling, tearing and/or eye discharge, light sensitivity, blurred vision and pain that doesn’t improve after removal of the contacts. If you have symptoms like this, remove the contacts and get medical assistance.
Remember to pause before inserting anything in your eyes. The consequences of bad decisions can be devastating and irreversible. I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: What Should NOT Be in Your Medicine Cabinet
Ever notice that people run straight to the medicine cabinet to do harm to themselves or others? I want you to know the harder the effort is to obtain items to hurt oneself, the less likely one is to follow through on the notion. On another related note, here’s a quick not-so-fun-but-interesting fact. One of the differences between America and say, certain European countries is the oversized influence of corporations in the States. Why am I talking about that on a medical blog? Read on. If you can’t tell where I’m going with this, you’ll get it pretty quickly.
Here’s my top five items I want you to take out your medicine cabinets and lock up.
1. Any jumbo sized container of any medication. Think about two of the most common over the counter (OTC) medications used for suicide attempts: acetaminophen (Tylenol) and salicylate (aspirin). One thing they have in common is you can buy what amounts to a tub-full of it at your local superstore in the United States. They should call these things ‘suicide quantities’, because often those in the midst of a suicide attempt will grab and swallow whatever is convenient. Many different medications will hurt you if you take enough; Tylenol and aspirin certainly fit that bill. Observing that (and additional considerations after the deaths due to the lacing of Tylenol with cyanide back in 1983), the Brits decided to not only pass a law limiting quantities, but certain medications that are high-frequency and high-risk for suicide use are now mandatorily dispensed in those annoying containers that you have to pop through the plastic container. Needless to say, observed suicide rates by medication rates plummeted as a result. Wonder why that hasn’t been implemented in the good ol’ USA?
2. Have teens in your house? Lock up the Robitussin and NyQuil. Dextromethorphan is the active ingredient in over 100 OTC cold and cough preparations. Teens use these to get high, folks. To make matters worse, they are addictive, and if taken with alcohol or other drugs, they can kill you. Then there’s ‘purple drank’ (yes, that’s how it’s spelled), in which these cough syrups containing codeine and promethazine (Benadryl) are mixed with drinks such as Sprite or Mountain Dew.
3. Have any sexual performance medications? This is part of a category of medicines called ‘medicines that can kill someone with just one pill’. That usually refers to kids or the elderly, but remember that those sexual enhancement drugs are medicines that lower your blood pressure. In the wrong person and in the wrong dose, taking such medicine – whether intentionally or accidentally – could be the last thing someone does.
3. Any narcotic. Need I say more? Remember, you do have people rummaging through your cabinets on occasion!
4. Any sharps. That includes sewing pins, needles, etc.
5. Any medication with an expiration date. The medication date actually is more of a ‘freshness’ consideration than a danger warning. However, in the wrong patient, a medicine that has less than the 100% guarantee of its needed strength that the expiration date represents could be fatal. Play it safe and get a new prescription.
There’s a lot more that could be added to this list, but I like keeping things manageable for you. Please childproof all your cabinets, and use childproof caps on your medications. I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Ever notice that people run straight to the medicine cabinet to do harm to themselves or others? I want you to know the harder the effort is to obtain items to hurt oneself, the less likely one is to follow through on the notion. On another related note, here’s a quick not-so-fun-but-interesting fact. One of the differences between America and say, certain European countries is the oversized influence of corporations in the States. Why am I talking about that on a medical blog? Read on. If you can’t tell where I’m going with this, you’ll get it pretty quickly.
Here’s my top five items I want you to take out your medicine cabinets and lock up.
1. Any jumbo sized container of any medication. Think about two of the most common over the counter (OTC) medications used for suicide attempts: acetaminophen (Tylenol) and salicylate (aspirin). One thing they have in common is you can buy what amounts to a tub-full of it at your local superstore in the United States. They should call these things ‘suicide quantities’, because often those in the midst of a suicide attempt will grab and swallow whatever is convenient. Many different medications will hurt you if you take enough; Tylenol and aspirin certainly fit that bill. Observing that (and additional considerations after the deaths due to the lacing of Tylenol with cyanide back in 1983), the Brits decided to not only pass a law limiting quantities, but certain medications that are high-frequency and high-risk for suicide use are now mandatorily dispensed in those annoying containers that you have to pop through the plastic container. Needless to say, observed suicide rates by medication rates plummeted as a result. Wonder why that hasn’t been implemented in the good ol’ USA?
2. Have teens in your house? Lock up the Robitussin and NyQuil. Dextromethorphan is the active ingredient in over 100 OTC cold and cough preparations. Teens use these to get high, folks. To make matters worse, they are addictive, and if taken with alcohol or other drugs, they can kill you. Then there’s ‘purple drank’ (yes, that’s how it’s spelled), in which these cough syrups containing codeine and promethazine (Benadryl) are mixed with drinks such as Sprite or Mountain Dew.
3. Have any sexual performance medications? This is part of a category of medicines called ‘medicines that can kill someone with just one pill’. That usually refers to kids or the elderly, but remember that those sexual enhancement drugs are medicines that lower your blood pressure. In the wrong person and in the wrong dose, taking such medicine – whether intentionally or accidentally – could be the last thing someone does.
3. Any narcotic. Need I say more? Remember, you do have people rummaging through your cabinets on occasion!
4. Any sharps. That includes sewing pins, needles, etc.
5. Any medication with an expiration date. The medication date actually is more of a ‘freshness’ consideration than a danger warning. However, in the wrong patient, a medicine that has less than the 100% guarantee of its needed strength that the expiration date represents could be fatal. Play it safe and get a new prescription.
There’s a lot more that could be added to this list, but I like keeping things manageable for you. Please childproof all your cabinets, and use childproof caps on your medications. I welcome your questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Straight, No Chaser: What Should Be in Your Medicine Cabinet

You’ve all done it. I’ve caught a few of you doing it. Why do you rummage through someone’s else’s medicine cabinet? Are newer homes even built with medicine cabinets anymore? Oh well… Today, I’m tackling a simple but important question in an ongoing effort to better empower you.
1. What should be in my medicine cabinet? Here’s my top five and why.
- Aspirin (324 mg). On the day you’re having a heart attack, you’ll want this available to pop in your mouth on the way to the hospital. Of all the intervention done in treating heart attacks, none is better than simply taking an aspirin. It offers a 23% reduction in mortality due to a heart attack by itself.
- Activated charcoal. This one may surprise you. Talk to your physician or pharmacist about this. If someone in your family ever overdoses on a medicine, odds are this is the first medication you’d be given in the emergency room. The sooner it’s onboard, the sooner it can begin detoxifying whatever you took. That said, there are some medications and circumstances when you shouldn’t take it, so get familiar with it by talking with your physician.
- Antiseptics such as triple antibiotic ointment for cuts, scratches and minor burns. It should be embarrassing for you to spend $1000 going to an emergency room when you could have addressed the problem at home. I guess I should include bandages here as well.
- A variety pack for colds, including antihistamines (like diphenhydramine, aka benadryl) and cough preparations. As a general rule, give yourself 3-5 days of using OTC preparations for a cold to see if it works or goes away. If not, then it’s certainly appropriate to get additional medical care. I guess I can lump a thermometer in this bullet point.
- The fifth item would be this number: 800-222-1222, which is number to the national poison control center. They will address your concerns, route you to your local poison center and help coordinate your care when you go to your emergency department.

You’ve all done it. I’ve caught a few of you doing it. Why do you rummage through someone’s else’s medicine cabinet? Are newer homes even built with medicine cabinets anymore? Oh well… Today, I’m tackling a simple but important question in an ongoing effort to better empower you.
1. What should be in my medicine cabinet? Here’s my top five and why.
- Aspirin (324 mg). On the day you’re having a heart attack, you’ll want this available to pop in your mouth on the way to the hospital. Of all the intervention done in treating heart attacks, none is better than simply taking an aspirin. It offers a 23% reduction in mortality due to a heart attack by itself.
- Activated charcoal. This one may surprise you. Talk to your physician or pharmacist about this. If someone in your family ever overdoses on a medicine, odds are this is the first medication you’d be given in the emergency room. The sooner it’s onboard, the sooner it can begin detoxifying whatever you took. That said, there are some medications and circumstances when you shouldn’t take it, so get familiar with it by talking with your physician.
- Antiseptics such as triple antibiotic ointment for cuts, scratches and minor burns. It should be embarrassing for you to spend $1000 going to an emergency room when you could have addressed the problem at home. I guess I should include bandages here as well.
- A variety pack for colds, including antihistamines (like diphenhydramine, aka benadryl) and cough preparations. As a general rule, give yourself 3-5 days of using OTC preparations for a cold to see if it works or goes away. If not, then it’s certainly appropriate to get additional medical care. I guess I can lump a thermometer in this bullet point.
- The fifth item would be this number: 800-222-1222, which is number to the national poison control center. They will address your concerns, route you to your local poison center and help coordinate your care when you go to your emergency department.