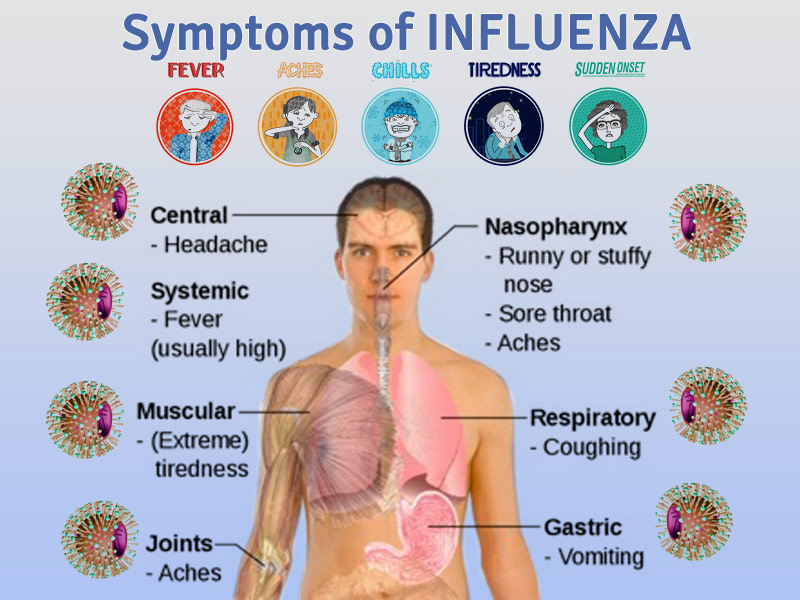
Does the flu shot give you the flu?
No, no, no. The influenza vaccine cannot cause flu illness. There are vaccines that involve the delivery of live virus, including mumps, measles, rubella, chicken pox and polio. Influenza is not in that category. Flu shots are made either with ‘inactivated’ vaccine viruses that are not infectious or they contain no flu vaccine viruses at all (and instead have recombinant particles that serve to stimulate your immune system).
The most common side effects from the influenza shot are soreness, redness, tenderness or swelling where the shot was given. Low-grade fever, headache and muscle aches also may occur. These symptoms are among the same symptoms you see with influenza, so it’s easy to confuse them as flu symptoms. They are not.
Controlled medical studies have been performed on humans in which some people received flu shots and others received shots containing salt water. There were no differences in symptoms other than increased redness and soreness at the injection site for those receiving influenza vaccine. The flu shot does not give you the flu.
I swear I’ve gotten the flu right after getting the flu shot! How is that possible if I can’t get the flu from the flu shot?
I always remind people that the flu vaccine does an even better job of preventing you from dying from the flu than it does in preventing you from catching the flu (and it does that at a 70–90% rate). It primes your immune system to better fight off the influenza virus when you’re exposed to it.
There are several reasons why someone still might get a flu-like illness after being vaccinated against the flu:
- Influenza is just one group of respiratory viruses. There are many other viruses that cause similar symptoms including the common cold, which is also most commonly seen during “flu season.” The flu vaccine only protects against influenza, so any other infection timed correctly can give you similar symptoms.
- When you get immunized against influenza, it takes the body up to two weeks to obtain the desired level of protection. There is nothing preventing you from having been infected before or during the period immediately before immunity sets in. Such an occurrence will result in your obtaining the flu despite being vaccinated.
- An additional reason why some people may experience flu-like symptoms despite getting vaccinated is that they may have been exposed to a strain of influenza that is different from the viruses against which the vaccine is designed to protect. The ability of a flu vaccine to protect a person depends largely on the match between the viruses selected to make the vaccine and those causing illness among the population that same year.
- It is also the case that the flu vaccine doesn’t always provide adequate protection against the flu. This is more likely to occur among people that have weakened immune systems or people age 65 and older. Even if the vaccine is 90% effect, some individuals will contact the flu despite having been vaccinated.
Please don’t get the wrong message from this section. These explanations are the exceptions, not the rule. In the overwhelming number of cases, the influenza vaccine does an excellent job of protecting against and prevent disease from the influenza virus.
Is it better to get the flu than the flu vaccine?
No. Influenza causes tens of thousands of deaths every year. If you have asthma, diabetes, heart disease or are especially young or old, you are placing yourself at significant risk by not getting vaccinated. Even if you aren’t in one of the above categories and are otherwise healthy, a flu infection can cause serious complications, including hospitalization or death.
Why do I need a flu vaccine every year?
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends a yearly flu vaccine for just about everyone six months and older. Once vaccinated, your immune protection decreases over time. These boosters are scheduled and dosed to help you maintain the best level of protection against influenza. Additionally, the virus mutates (changes) every year, so what you were covered for this year may not apply next year.
You can make a decision not to get vaccinated, and Straight, No Chaser has posted tips for you to protect yourself in the event you choose not to. (Click here to review.) However, you’re doing so in the face of the solid consensus of medical evidence and research. You should seriously question the motives or knowledge of someone who suggests that you should not get vaccinate for influenza, particularly if they profess to be involved in healthcare. Get vaccinated.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com offers. Please share our page with your friends on WordPress. We are also on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and Twitter at @asksterlingmd.