Several of you asked about the treatment of the eye conditions resulting from diabetes. This last Straight, No Chaser addressing Diabetes Awareness Month will focus on treatment approaches.
The first point – and one that can’t be overemphasized – is treatment is not a cure. As long as diabetes continues (and especially continues to be uncontrolled), symptoms will progress, and the diabetic-related causes of eye disorders will create ongoing difficulties, even after treatment of past problems has occurred. Thus, the first consideration is to understand steps you can take to prevent or slow the progression of the effects of diabetes on your eyes.
There actually are several preventive measures within your control. Consider implementing these.
- Keep your blood glucose and blood pressure as close to normal as you can. This involves dieting, exercising and taking your medication as prescribed.
- Have an eye care professional examine your eyes annually – even if your vision is normal, and especially if your vision is normal. If you have good control of your diabetes, your eyes will tell part of that story, and you need to stay ahead of evolving problems. Of course, discovering problems early and getting prompt treatment gives you the best opportunity to maintain normal vision and to prevent advancement to more serious stages. Be proactive and ask your eye care professional to check for signs of cataracts and glaucoma.
- If you are diabetic and planning to get pregnant, ask your doctor if you should have an eye exam.
- If you are diabetic and pregnant, see an eye care professional during your first 3 months of pregnancy.
- Don’t smoke.
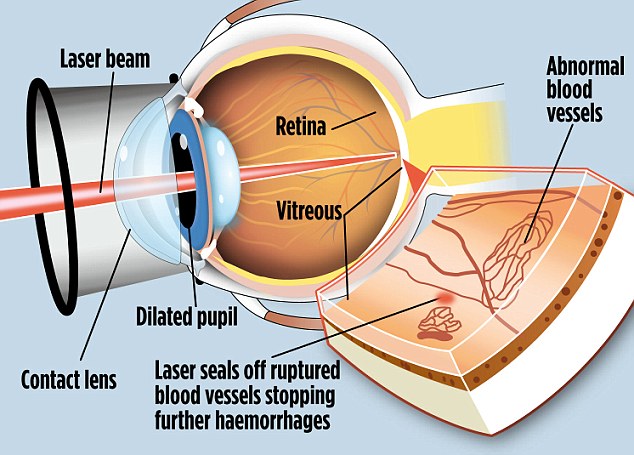
Recall that damaged older vessels or fragile new vessels has a propensity to bleed into the eye. This blood interferes with your ability to see normally. This severe, advanced diabetic retinopathy is treated with laser surgery, which helps to shrink the abnormal blood vessels, thus reducing bleeding into the eye. The procedure involves 1,000 to 2,000 laser burns in the area of the retina (the lining in the back of your eye that senses light), causing the abnormal blood vessels to shrink. Even as laser surgery saves much of your sight, patients often notice reduction or loss of side vision, color vision and/or night vision.
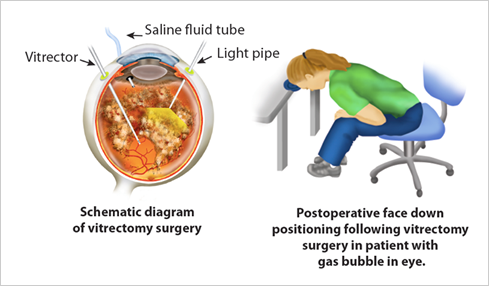
If the bleeding is especially severe, you may need a surgical procedure called a vitrectomy. This procedure removes blood from the center of your eye.
These procedures stabilize vision and in some instances may dramatically improve it. Focal laser treatment reduces the risk of vision loss by 50 percent and the risk of blindness by 90 percent. However, laser surgery most often cannot restore vision that has already been lost. That is why finding diabetic retinopathy early should be your most important strategy to prevent vision loss. There are additional medical treatment options emerging meant to replace the need for surgery. If you suffer from diabetic retinopathy, discuss these options with your eye doctor.
Please remember, that although both laser treatments and vitrectomies are very effective in reducing vision loss, they are not cures. Once you have proliferative retinopathy, you always will be at risk for new bleeding. That said, people with progressive diabetic retinopathy have less than a five percent chance of becoming blind within five years of early treatment.
Please use the preventive strategies and understand the treatment options available to you. Failure to do so could be devastating.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what 844-SMA-TALK and http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com(SMA) offers. Please share our page with your friends on WordPress, Facebook @ SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2014 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress