With all the focus of late on other forms of drug use and abuse (e.g., methamphetamine, marijuana), alcohol abuse seems to be lacking the attention it deserves. Fully one in six people in the United States has a drinking problem. In this segment of the Straight, No Chaser series on alcohol, we will explore problem drinking.
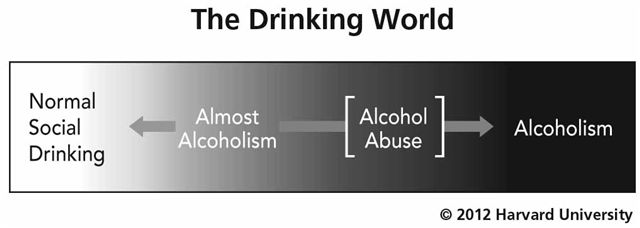
“Problem drinking” is a way of describing alcohol intake that causes problems with your functioning. Alcohol abuse is an episode or continued excessive alcohol consumption that causes problems with your daily living activities, such as family or job responsibilities. Of course, a single episode of alcohol abuse can cost you your life if you’re an impaired driver who runs into a tree or some other calamity befalls you.
Alcoholism is alcohol dependence, which is comprised of two separate considerations:
- Physical addiction to a drug is defined by tolerance and withdrawal symptoms. Tolerance is when you become acclimated to the same dose of drug, meaning, in this case, the same amount of liquor no longer gives you the same buzz. Withdrawal symptoms occur when you experience effects from no longer having the drug in your system.
- Mental addiction to alcohol is illustrated by its increasingly prominent role in your life. Your life becomes centered around the pursuit and consumption of alcohol. It creates problems with your physical, mental and social health, controlling your life and relationships.
Many of you ask if alcoholism is hereditary. Hereditary means a specific thing medically, so the answer is no. However, we believe genes play a role and increase the risk of alcoholism. It is most likely that genetics “load the gun,” but environment “pulls the trigger.”
Regarding environment, there’s no fixed equation to if and when you’ll become dependent, but there is a correlation with certain activity and an increased risk. Consider the following activities as suggestive of a significant risk for development alcoholism:
- Men who have 15 or more drinks a week (One drink is either a 12-ounce bottle of beer, a 5-ounce glass of wine or a 1.5 ounce shot of liquor.)
- Women who have 12 or more drinks a week
- Anyone who has five or more drinks at a time at least once a week
- Anyone who has a parent with alcoholism
Here are some less hard signs, but these situations also have been shown to increase risk, according to the National Institutes of Health:
- You are a young adult under peer pressure
- You have a behavioral health disorder such as depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, or schizophrenia
- You have easy access to alcohol
- You have low self-esteem
- You have problems with relationships
- You live a stressful lifestyle
- You live in a culture in which alcohol use is more common and accepted
Feel free to contact your SMA expert consultant if you have any questions on this topic.
Thanks for liking and following Straight, No Chaser! This public service provides a sample of what http://www.SterlingMedicalAdvice.com (SMA) and 844-SMA-TALK offers. Please share our page with your friends on WordPress. We are also on Facebook at SterlingMedicalAdvice.com and Twitter at @asksterlingmd.
Copyright © 2015 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC