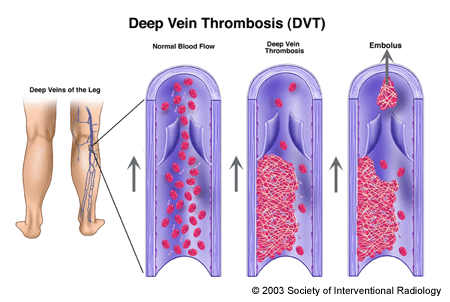
When patients talk about blood clots, they’re describing a blockage of a blood vessel somewhere in the body, usually the lower extremities (legs and thighs), the lungs (pulmonary embolus) or the brain. Today we’ll discuss the variety that occurs in the lower extremities, which are generally referred to as deep venous thrombosis (DVTs). In case you’re thinking that a clot in the leg doesn’t sound as bad as a clot in the lungs or the head, you’re correct – until you understand that DVTs break off and travel to other body sites, leading to blockage elsewhere (This is called embolism.).
Your challenge is to appreciate the risks of developing DVTs and the symptoms. Risk factors include the following:
- Birth control pills or other estrogen use (this combined with cigarette smoking pushes the risk even higher)
- Cancer
- Cigarette smoking
- Family history of blood clots
- Obesity
- Prolonged immobilization
- Recent pelvic or leg fracture
- Recent surgery (most often the pelvis or lower extremities)
- Recent travel involving long periods of sitting
- Certain medical conditions, most notably lupus
Symptoms most commonly are in one leg or the other, and reflect the fact that the vein is being blocked. These include pain, swelling, redness and warmth.
Diagnosis and treatment are relatively straightforward as long as they occur in time (meaning before the clots have broken off). Diagnosis is usually accomplished by an ultrasound of the lower extremities; once discovered, you’ll be placed on blood thinners. It’s important to know that blood thinners prevent the formation of new clots. They do not dissolve existing clots. That’s usually not necessary, as many DVTs simply dissolve. If it doesn’t, DVTs that embolize are life-threatening (more so from the pelvis and thigh than the legs). Unfortunately pulmonary emboli are among the most missed medical diagnoses and causes of death. Try to manage your controllable risk factors, and be aware when you’re dealing with a risk factor that you can’t control (like surgery).
I welcome any questions or comments.
Copyright © 2013 · Sterling Initiatives, LLC · Powered by WordPress
Dr. Sterling….you said that diagnosis and treatment are pretty straightforward as long as the clots have not broken off. What is the difference in treatment? And, why is it more difficult if they’ve broken off?
Hi, Stephanie. Consider the mechanics of it all. Clots are different sizes. A clot attached to your leg may or may not produce symptoms. Once a clot detaches, it’s called an embolus and will usually float around until it meets resistance. If this occurs in the brain, the resulting blockage can cause a stroke. If it occurs in the lungs, it can impede your breathing. Treatment of an embolus can range from treating the clot to treating the stroke. Depending on the severity, sometimes clot-busting agents are needed. Thanks for the question and following Straight, No Chaser.